Introduction
An overburden is known as the dumping of coal mine tailings and other reject materials. It is nutrient-poor, contains elevated concentrations of trace metals and loosely adhered particles of shale, stones, and boulders, and is devoid of true soil characteristics (Dowarah et al., 2009; Novianti et al., 2018). Therefore, the presence of plants on the overburden (OB) is crucial, because not all species can colonize the sites under these conditions, and their presence may facilitate the presence of subsequent species. Some plants do grow on the OB (Novianti et al., 2017). However, a few of these have been identified as exotic species.
Invasion by exotic plant species in an ecosystem is considered a threat because of the deleterious effects they have for people and nature (Kawaletz et al., 2013; Setyawati et al., 2015), and exotic species should be removed or killed whenever possible. However, the potential consequences of invasive species vary widely across ecosystems (Pejchar & Mooney, 2009), and for both people and nature (Koutika & Richardson, 2019). In Indonesia, there are more than 2000 exotic species, 300 of which are classified as invasive (Setyawati et al., 2015), indicating that possibly not all exotic species are invasive. According to Woods and Mariarty (2001), the role of exotic species is unclear.
In previous studies, 123 plant species have been identified from OB (Novianti et al., 2017). The aim of this study was to classify the species in the OB as native and exotic, and to determine the role of the exotic species. Relative coverage was used to determine the dominance of the species. In primary succession, coverage of species may be more representative in describing the dominance of space than the density of species. OB is presented as a model system to study primary succession (Prach et al., 2013) because it is one of the most important human-mediated disturbances that create this condition.
Information about plant species and their roles is essential to understand succession and restoration. An understanding of succession can used as a tool for restoration efforts (Kangas, 2004) because it can be used to accelerate natural succession (Bradshaw, 1987). Therefore, it is necessary to investigate changes in species composition and associated substrates over time to manipulate succession (Dowarah et al., 2009; Novianti, 2020; Walker et al., 2007).
Materials and Methods
Description of study area
The study was conducted in a coal OB dumping area located in Satui District, South Kalimantan, Indonesia. The sampling was carried out on an out-pit dump (i.e., on an OB dumped at certain disposal sites outside of the mine pit), and without leveling on its surface (known as free dump). The determination of OB heaps was based on the following conditions: (1) no disposal process (final dump), (2) known age, (3) identified origin depth, and (4) identified geological formation. According to this, six OBs were used as the study area of primary succession using a chronosequence approach (Table 1).
Vegetation analysis
OB heaps of different ages were selected, that is, 7, 10, 11, 42, 59, and 64 months old. A vegetation study was conducted using the line-transect method. For each transect, the line-intercept method was used (Mueller-Dombois & Ellenberg, 1974); each plant species that was covered by the transect line was recorded, and plant coverage was estimated by measuring the width of each individual from the transect line. This coverage measurement can produce >100% coverage because of overlapping plants. The number of transect lines was adjusted according to the length of the area with a distance between lines of 5 m, while the length of the transect line followed the width of each area (Novianti et al., 2017; 2018).
Species identification
All vegetation was identified using information from the local communities, plant identification books, and environmental impact assessment reports of PT. AI Satui Mine Project, and websites. Exotic and native species and the origin region were identified based on the identification books of Flora van Java (Van Steenis, 1992), a guidebook for invasive alien plant species in Indonesia (Setyawati et al., 2015), and websites ( https://powo.science.kew.org/).
Data analysis
Data for the native and exotic species were analyzed descriptively. The relationship between the number of species and time was analyzed using linear correlation at a significance level of 5% (α=5%). The range of vegetation was calculated for each species at each site, including coverage and relative coverage, to determine dominance.
Results
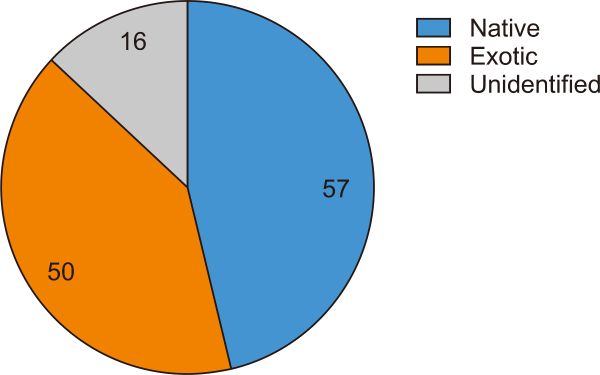
The numbers of native and exotic plant species were 57 and 50, respectively. Sixteen species were not identified (Fig. 1). The native species present at all ages of the OB embankment were Cyperus sulcinux, Fimbristylis dichotoma, Paspalum scrobiculatum, Rhyncospora corymbosa, Scleria sumatrensis (herb), and Trema orientalis (shrub). The exotic species consisted of Echinochloa colona, Leersia hexandra, Paspalum conjugatum, Paspalum dilatatum (herbs), Chromolaena odorata, Clibadium surinamense, and Trema micrantha (shrub) (Table 2).
Neither the number of exotic species (r=0.7093, N=6, P<0.05) nor the number of native species (r=0.7051, N=6, P<0.05) showed a significant relationship with time. However, the number of native species tended to be higher than that of exotic species over time (Fig. 2). Based on the species dominance, Paspalum conjugantum, an exotic plant dominated in the first five heap ages and was replaced at 64 months of stockpiling by Neyraudia reynaudiana, a native species. Meanwhile, other species dominated only at a certain age of the heap spoil (Table 3). The relative dominance of native (r=0.0954, N=6, P<0.05) and exotic (r=0.2512, N=6, P<0.05) species did not significantly correlate with time (Fig. 3). In addition, the dominance of exotic species was higher than that of native species at all six stockpile ages. A community dynamic relationship was observed between exotic and native species, that is, a decrease in the percentage coverage area by exotic species was followed by an increase in the percentage coverage area by native species. The decrease in spatial control by exotic species and increase in dominance by native species began to occur at 59 months of stockpiling age.
Discussion
This study showed that both native and exotic species are present at an early successional stage in OB stockpiles. A higher percentage of native species indicated that seed sources were still available. They can be a source for pioneer vegetation during restoration, considering that the plant species used are generally brought from outside Indonesia, such as Centrosema pubescens (Hindersah et al., 2021). Moreover, the surroundings of the mine have been dominated by fast-growing trees, such as Acacia mangium, as the main tree used in reclamation (Lewis et al., 2022). The native species present throughout the heap were herbs, such as sedges, grasses, and trees, whereas exotic plants were grasses, shrubs, and trees. The presence of plants in the early stages of primary succession is influential because they must cope with unfavorable conditions for establishment. Their growth and distribution are often restricted by nutrient availability because of bare substrates (Dalling, 2008; Glenn-Lewin et al., 1992; Novianti et al., 2018). Furthermore, when these plants die, they become an organic source that will improve substrate conditions, increase safe microsites over time, and consequently increase the number of species (Marrs & Bradshaw, 1993; Novianti, 2013; Walker & del Moral, 2011).
Initially, exotic species dominated both in terms of the number of species and their coverage, perhaps because of their higher response (per capita growth) to the opportunities of niche and resources than that of the resident species (Shea & Chesson, 2002). However, the number of species and the coverage of native species increased with time. Once a surface is colonized, future generations of colonists are likely to be controlled by local seed production or vegetative expansion, and the disturbance may be colonized in successively expanding plant nuclei (Walker & dan del Moral, 2011).
Some native and exotic have roles as pioneers and some as “followers” in the chronosequence of the OB spoil. Pioneers are those that arrive and grow quickly on very poor substrata and appear to facilitate the subsequent vegetation; “followers” are the ones that appear subsequently (Novianti, 2020; Novianti et al., 2018). Temporary dominance by native and exotic plants shows a temporal pattern during succession in post-mining landscapes (Baasch, 2010). These results indicate that both native and exotic species assist in primary succession. These processes may take longer without their presence during the early primary succession. Herbs are present and dominate at the beginning of succession (Dalling, 2008). In addition, shrubs and trees colonize very quickly and dominate after only 64 months, probably because of their close proximity to a diverse species pool and the constant high spoil moisture content (Maharana & Patel, 2013; Novianti et al., 2018).
In conclusion, the species that predominate at the beginning of primary succession in the OB of coal mines are exotic species. The temporary presence of exotic species assists the primary succession process in OB areas by improving the condition of the OB substrate, without which the succession process may possibly take longer. These results indicate that not all exotic species are invasive. Information about the role of exotic species in primary succession is needed as part of the integration between scientific and management concerns for practical knowledge in doing restoration.
Figures and Tables
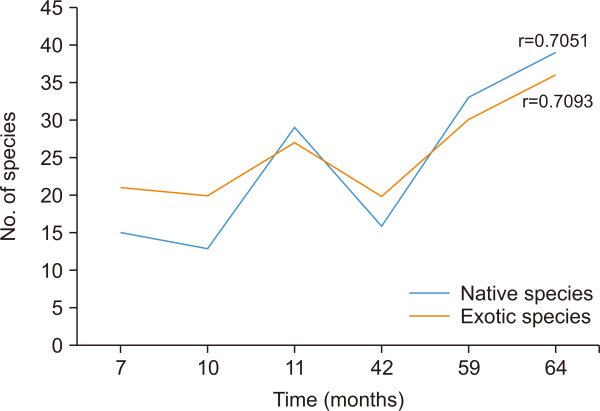
Correlation between time (months) and number of native and exotic species on the chrono sequence on coal overburden spoils
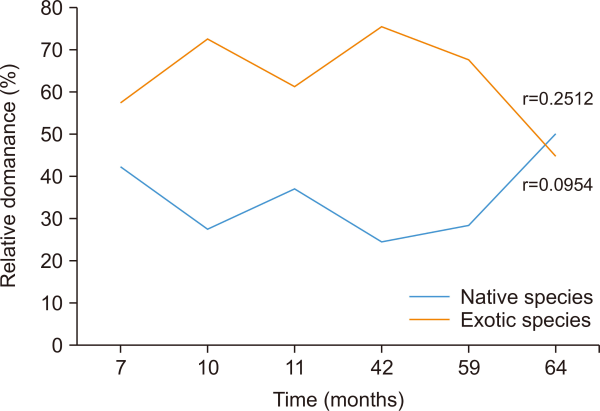
Correlation between time (months) and total relative dominance of native and exotic species on the chronosequence on coal overburden spoils.

Native and exotic plant species and their relative dominances on the chronosequence on coal overburden spoils