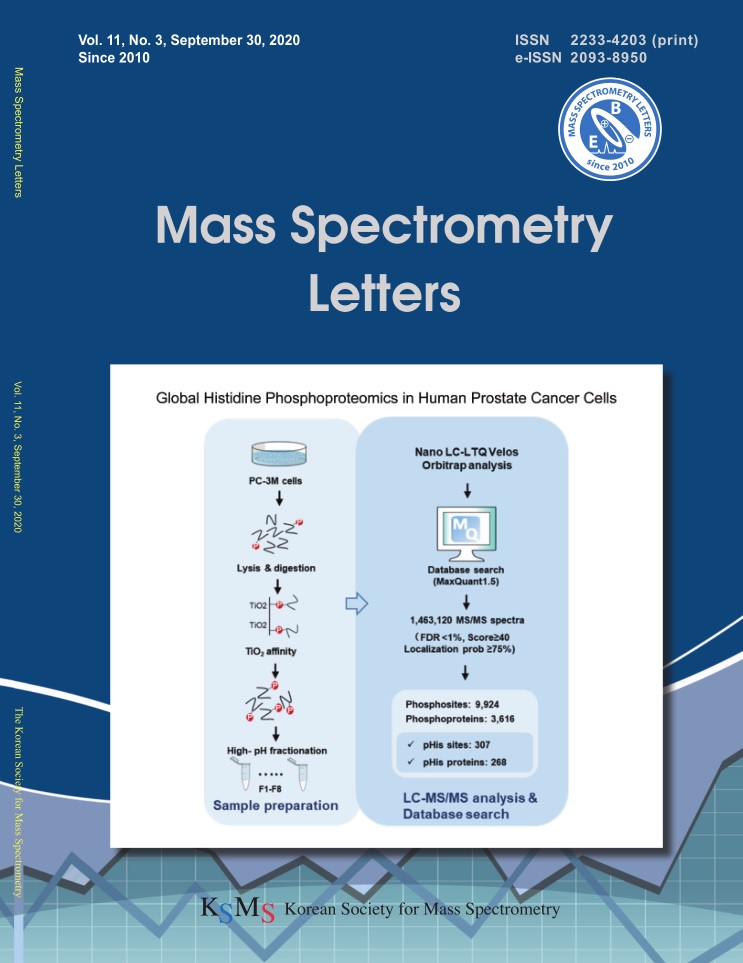
Global Histidine Phosphoproteomics in Human Prostate Cancer Cells
Mass Spectrometry Letters / Mass Spectrometry Letters, (P)2233-4203; (E)2093-8950
2020, v.11 no.3, pp.52-58
https://doi.org/10.5478/MSL.2020.11.3.52
Gao Yan
(Kyungpook National University)
Kim Doeun
(Kyungpook National University)
Sung Eunji
(Kyungpook National University)
Tan Minjia
(Kyungpook National University)
Kwon Tae Gyun
(Kyungpook National University)
Lee Jun Nyung
(Kyungpook National University)
Lee Sangkyu
(Kyungpook National University)

Gao,
Y., Kim,
D., Sung,
E., Tan,
M., Kwon,
T. G., Lee,
J. N., &
Lee,
S.
(2020). Global Histidine Phosphoproteomics in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. , 11(3), 52-58, https://doi.org/10.5478/MSL.2020.11.3.52
- 675Downloaded
- 1,321Viewed
Abstract
Histidine phosphorylation (pHis) is increasingly recognized as an important post translational modification (PTM) in regulating cellular functions in eukaryotes. In order to clarify the role of pHis in mammalian cell signaling system, a global phos-phorylation study was performed in human prostate cancer cells, PC-3M, using a TiO 2 affinity chromatography. A total number of 307 pHis sites were identified on the 268 proteins among total identified 9,924 phosphorylation sites on 3,316 proteins. In addition, 22 pHis proteins were classified in enzyme category. This report provides the first database for the study of pHis in prostate cancer cells.
- keywords
-
Histidine phosphorylation,
TiO 2 -affinity chromatography,
Mammalian cells,
LC-MS
- Submission Date
- 2020-07-18
- Revised Date
- 2020-09-03
- Accepted Date
- 2020-09-03