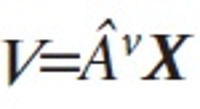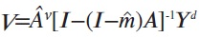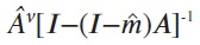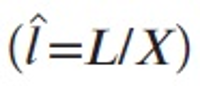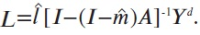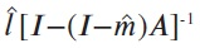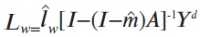ISSN : 2287-9099
Vol.1 No.3

Abstract
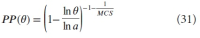
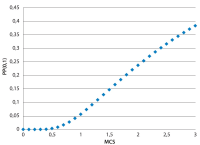
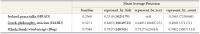
A new explanation, using exponential functions, is given for the S-shaped functional relation between the mean citation score and the proportion of top 10% (and other percentages) publications for the 500 Leiden Ranking universities. With this new model we again obtain an explanation for the concave or convex relation between the proportion of top 100θ% publications, for different fractions of θ.



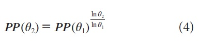




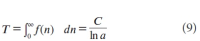

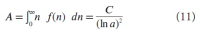

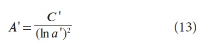
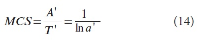

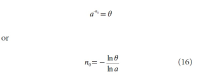
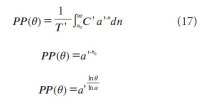
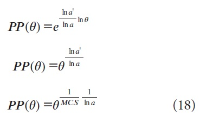
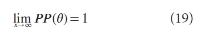

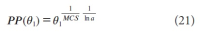
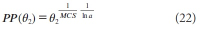
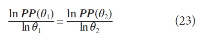



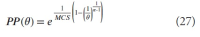
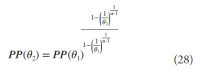


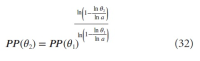
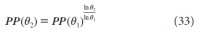
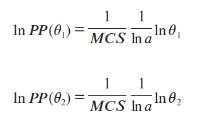
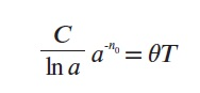

Abstract
The paper introduces the research area of interactive information retrieval (IIR) from a historical point of view. Further, the focus here is on evaluation, because much research in IR deals with IR evaluation methodology due to the core research interest in IR performance, system interaction and satisfaction with retrieved information. In order to position IIR evaluation, the Cranfield model and the series of tests that led to the Cranfield model are outlined. Three iconic user-oriented studies and projects that all have contributed to how IIR is perceived and understood today are presented: The MEDLARS test, the Book House fiction retrieval system, and the OKAPI project. On this basis the call for alternative IIR evaluation approaches motivated by the three revolutions (the cognitive, the relevance, and the interactive revolutions) put forward by Robertson & Hancock-Beaulieu (1992) is presented. As a response to this call the ‘IIR evaluation model’ by Borlund (e.g., 2003a) is introduced. The objective of the IIR evaluation model is to facilitate IIR evaluation as close as possible to actual information searching and IR processes, though still in a relatively controlled evaluation environment, in which the test instrument of a simulated work task situation plays a central part.


Abstract
Despite limited success, today’s information retrieval (IR) systems are not intelligent or reliable. IR systems return poor search results when users formulate their information needs into incomplete or ambiguous queries (i.e., weak queries). Therefore, one of the main challenges in modern IR research is to provide consistent results across all queries by improving the performance on weak queries. However, existing IR approaches such as query expansion are not overly effective because they make little effort to analyze and exploit the meanings of the queries. Furthermore, word sense disambiguation approaches, which rely on textual context, are ineffective against weak queries that are typically short. Motivated by the demand for a robust IR system that can consistently provide highly accurate results, the proposed study implemented a novel topic detection that leveraged both the language model and structural knowledge of Wikipedia and systematically evaluated the effect of query disambiguation and topic-based retrieval approaches on TREC collections. The results not only confirm the effectiveness of the proposed topic detection and topic-based retrieval approaches but also demonstrate that query disambiguation does not improve IR as expected.

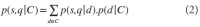
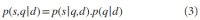
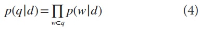
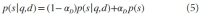
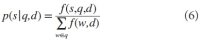
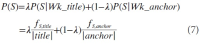
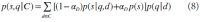


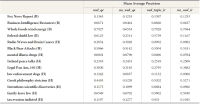
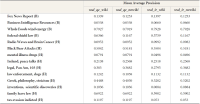

Abstract
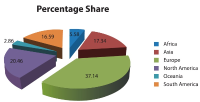
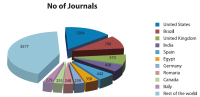
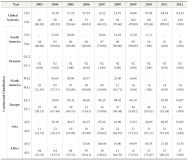
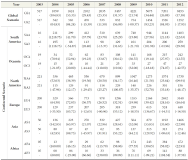
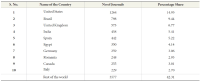
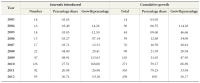
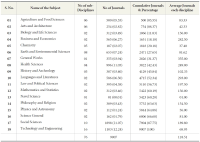
The present study aims to assess the growth of open access journals at a global level. The concept of Open Access (OA) publishing is being well received among academic circles and as a result we can see more and more scholarly content is being made these days available in open access format. The present study is simply an attempt to assess the trend and growth of open access journals during the last decade, viz. for the period 2003-2012, for which data has been retrieved from the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ), which as of date hosts more than 9700 journals from 120 countries across the world covering major languages of the world. But keeping in view the period of our study the data has been retrieved as per our applicability, which as a result confines our study to 8453 journals only. The directory covers 18 main subject areas having 76 sub-disciplines, each having on average 118.53 journals. During the entire decade the number of countries which entered into OA publishing rose from 49 to 120 with a growth of 144%, and if this growth rate continues to be the same for the next five years, viz. by 2018, the world will turn into 100% open access. At the continental level Europe leads the tally by publishing a maximum of 3140 OA journals contributed by 43 countries across Europe, which again is the highest number from any continent.


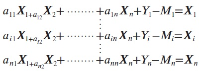
Abstract
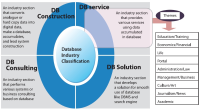
The Database Industry Promotion Act was proposed at the National Assembly plenary session on July 26, 2012 and since then it has been in the process of enactment in consultation with all the governmental departments concerned. The recent trend of economic globalization and smart device innovation suggests a new opportunity and challenges for all industries. The database industry is also facing a new phase in an era of smart innovation. Korea is in a moment of opportunity to take an innovative approach to promoting the database industry. Korea should set up a national policy to promote the database industry for citizens, government, and research institutions, as well as enterprises. Above all, the Database Industry Promotion Act could play a great role in promoting the social infrastructure to enhance the capacity of small and medium-sized enterprises. This article discusses the background of the development of the Database Industry Promotion Act and its legislative processes in order to clarify its legal characteristics, including the meaning of the act. In addition, this article explains individual items related to the overall structure of the Database Industry Promotion Act. Finally, this article reviews the economic effects of the database industry for now and the future.