Vol.10 No.4
Abstract
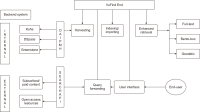
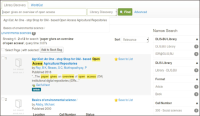
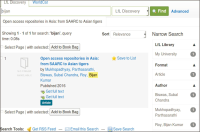
This paper provides an overview of the emergence of resource discovery systems and services, along with their advantages, best practices, and current landscapes. It outlines some of the key services and functionalities of a comprehensive discovery model suitable for academic libraries in developing countries. The proposed model (VuFind as a discovery tool) performs like other existing web-scale resource discovery systems, both commercial and open-source, and is capable of providing information resources from different sources in a single-window search interface. The objective of the paper is to provide seamless access to globally distributed subscribed as well as open access resources through its discovery interface, based on a unified index. This model uses Koha, DSpace, and Greenstone as back-ends and VuFind as a discovery layer in the front-end and has also integrated many enhanced search features like Bento-box search, Geodetic search, and full-text search (using Apache Tika). The goal of this paper is to provide the academic community with a one-stop shop for better utilising and integrating heterogeneous bibliographic data sources with VuFind (https://vufind.org/vufind).


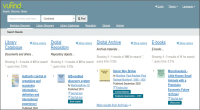
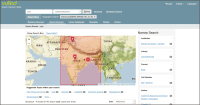
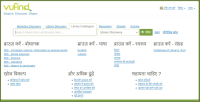
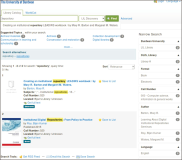
Abstract
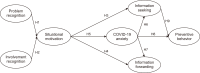
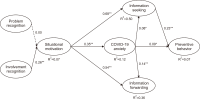
The pandemic of Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) has contributed more challenges for mothers as the family’s primary caregiver in overcoming the widespread infection. Pandemic-related information is essential for mothers to reduce uncertainty as well as to maintain the health of family members during this unprecedented situation. Adopting the framework of the Situational Theory of Problem Solving, this study extends the theory by, first, testing the mediating role of COVID-19 anxiety on mothers’ information seeking and information forwarding, referred to as active communication action of problem solving, as well as preventive behavior; and second, by predicting the effect of information seeking on preventive behavior. Referring to an online survey from 371 Indonesian mothers, the findings suggest that in terms of direct effect, only problem recognition was found to have no significant effect on situational motivation. The results suggest that Indonesian mothers perceive COVID-19 as personally relevant so that they are motivated to solve the problem by seeking and forwarding related information. In addition, COVID-19 anxiety was found to play a significant role in predicting information seeking, information forwarding, and preventive behavior. The result of this study is expected to give insights for risk communicators and health professionals in Indonesia in communicating COVID-19, particularly to mothers.

Abstract
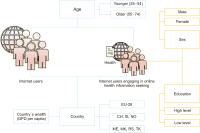
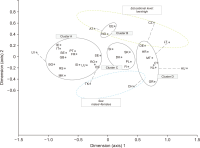
Since older people are traditionally considered disadvantaged when it comes to Internet use, it is useful to examine whether older individuals use the Internet for health information seeking (HIS). This study aims to investigate digital inequalities in terms of Internet use by older population for HIS in the European region. As methods, we applied secondary data analysis (of Eurostat data) to investigate the influence of age, educational level, sex, and countries’ wealth. Cluster analysis combined with multidimensional scaling was used to find out those countries exhibiting similarities in older people’s online HIS. The main results are: Older individuals do not equally use the Internet in general and for HIS in particular. Older Internet users with higher level of education and of the female sex are more likely to use the Internet for health information.





Abstract
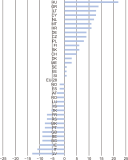
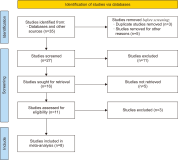
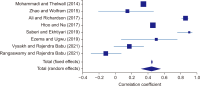
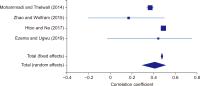
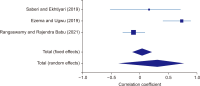
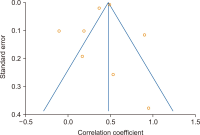
Altmetrics or alternative metrics gauge the digital attention received by scientific outputs from the web, which is treated as a supplement to traditional citation metrics. In this study, we performed a meta-analysis of correlations between classic citation metrics and altmetrics indicators of library and information science (LIS) articles. We followed the systematic review method to select the articles and Erasmus Rotterdam Institute of Management Guidelines for reporting the meta-analysis results. To select the articles, keyword searches were conducted on Google Scholar, Scopus, and ResearchGate during the last week of November 2021. Eleven articles were assessed, and eight were subjected to meta-analysis following the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The findings reported negative and positive associations between citations and altmetric indicators among the selected articles, with varying correlation coefficient values from -.189 to 0.93. The result of the meta-analysis reported a pooled correlation coefficient of 0.47 (95% confidence interval, 0.339 to 0.586) for the articles. Sub-group analysis based on the citation source revealed that articles indexed on the Web of Science showed a higher pooled correlation coefficient (0.41) than articles indexed in Google Scholar (0.30). The study concluded that the pooled correlation between citation metrics with altmetric indicators was positive, ranging from low to moderate. The result of the study gives more insights to the scientometrics community to propose and use altmetric indicators as a proxy for traditional citation indicators for quick research impact evaluation of LIS articles.

Abstract
The main aim of this study is to identify the role of information dissemination on urban and rural citizens of Bangladesh during the COVID-19 pandemic and the role of misinformation in this process. The study also aimed at finding appropriate counter misinformation strategies regarding COVID-19. An online questionnaire was prepared to collect the viewpoints of the urban and rural citizens of Bangladesh regarding dissemination of information during COVID-19, misinformation regarding COVID-19, and counter misinformation strategies. Along with demographic and general information, a five-point Likert scale was used to measure COVID-19 related misinformation beliefs and how to counter them. Chi square tests were used to determine the association between current residency, information sources, the importance of information dissemination, reactions after getting COVID related information, and evaluative steps after getting information and before disseminating it. Additionally, nonparametric Mann–Whitney U and Kruskal–Wallis tests were conducted to know the significance of difference in respondents’ assessment on COVID-19 related misinformation in terms of their demographic characteristics. Cronbach’s alpha score was obtained to see the reliability of the questionnaire items. The current study reveals that both urban and rural citizens of Bangladesh are influenced by information dissemination regarding COVID-19 and they have lower level of misinformation belief. The respondents have differences in misinformation belief by different demographic groups. Respondents’ educational status, information literacy, sources of getting information, and evaluative steps after getting information have significant differences in misinformation belief. The study also noticed the support of respondents for countering misinformation strategies regarding COVID-19.
Abstract
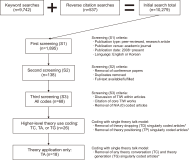
Previous studies have found that the use or development of theory in library and information science (LIS) research is comparatively low and may be trending downward. LIS has also been criticized for relying on theories imported from other disciplines rather than applying or developing theories from within. The theory of information worlds, a social information behavior theory originally introduced in 2008, represents a newer LIS theory whose level of adoption is understudied. This study features a systematic literature review of peer-reviewed research articles which cited or used the theory of information worlds from 2008 to early 2022 to identify trends related to levels of theory use, publication venues, author affiliations, countries, and collaborations, as well as research methods, topics, and populations. Findings suggest that both awareness and use of the theory of information worlds are positively trending, though at slower rates for higher levels of theory use, such as full applications of the theory to guide the collection and analysis of empirical data. The theory has also been used by researchers from around the world and across disciplines, most often with mixed and qualitative methods. While the growth of a new LIS theory is promising, the authors echo calls for increased use and development of the theory of information worlds, and other LIS theories more broadly, and as more interdisciplinary collaboration.