Vol.9 No.2
Abstract
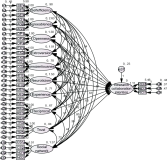
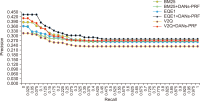
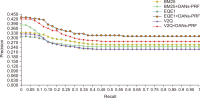
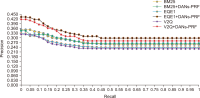
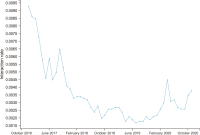
Pseudo relevance feedback (PRF) is a powerful query expansion (QE) technique that prepares queries using the top k pseudo-relevant documents and choosing expansion elements. Traditional PRF frameworks have robustly handled vocabulary mismatch corresponding to user queries and pertinent documents; nevertheless, expansion elements are chosen, disregarding similarity to the original query’s elements. Word embedding (WE) schemes comprise techniques of significant interest concerning QE, that falls within the information retrieval domain. Deep averaging networks (DANs) defines a framework relying on average word presence passed through multiple linear layers. The complete query is understandably represented using the average vector comprising the query terms. The vector may be employed for determining expansion elements pertinent to the entire query. In this study, we suggest a DANs-based technique that augments PRF frameworks by integrating WE similarities to facilitate Arabic information retrieval. The technique is based on the fundamental that the top pseudo-relevant document set is assessed to determine candidate element distribution and select expansion terms appropriately, considering their similarity to the average vector representing the initial query elements. The Word2Vec model is selected for executing the experiments on a standard Arabic TREC 2001/2002 set. The majority of the evaluations indicate that the PRF implementation in the present study offers a significant performance improvement compared to that of the baseline PRF frameworks.

Abstract
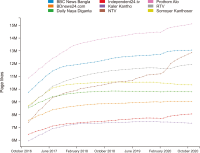
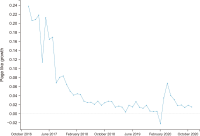
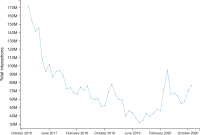
Social media has become a popular source of information around the world. Previous studies explored different trends of social media news consumption. However, no studies have focused on Bangladesh to date, where social media penetration is very high in recent years. To fill this gap, this research aimed to understand its popularity trends during the period. For that reason, this work analyzes 97.67 million page likes and 3.48 billion interaction data collected from nine Bangladeshi news media’s Facebook pages between December 2016 to November 2020. The analysis shows that the growth rates of page likes and interaction rates declined during this period. It suggests that the media’s Facebook pages are gradually losing their popularity among Facebook users, which may have two more interpretations: Facebook’s aggregate appeal as a news source is decreasing to users, or Bangladeshi media’s appeal is eroding to Facebook users. These findings challenge the previous results, i.e., Facebook’s demand as a news source is increasing with time. We offer four explanations of the decreased popularity of Facebook’s news: information overload, exposure to incidental news, users’ selective exposure and different aims of using Facebook, and conflict between media agendas and users’ interests. Some theoretical and practical significance of the results has been discussed as well.






Abstract
The purpose of this paper is to analyze the case of ‘drive-thru’ services newly introduced and tried in libraries in Korea under the influence of COVID-19, and to develop and propose a service model so that this service can be continuously applied to all libraries in the future. Therefore, the method of study was selected and analyzed by selecting one of the representative libraries that provide related services in Seoul Special City, Incheon Metropolitan City, and Anyang City of Gyeonggi Province. In addition, a focus group interview was conducted with twelve people in charge to find a way to apply the drive-thru service to the library. As a result, the library’s drive-thru service is a way to fulfill the library’s original purpose of providing information materials while minimizing faceto- face contact with users. It was concluded that it is a suitable method for a library of complex buildings, where there is a lack of parking space. In addition, it was deduced that it may be one of the ways to use the library efficiently for office workers who are unable to use library services during the opening hours. Therefore, if the drive-thru service is implemented according to the developed model, it is expected to increase the library visit rate and data utilization rate.

Abstract
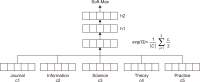
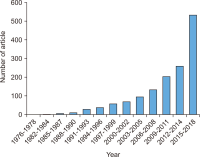
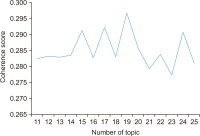
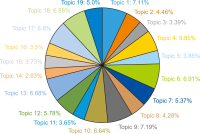
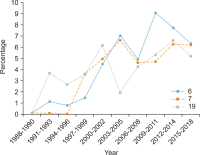
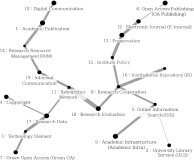
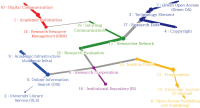
This study aims to identify specific topics, trends, and structural characteristics of scholarly communication research, based on 1,435 articles published from 1970 to 2018 in the Scopus database through Latent Dirichlet Allocation topic modeling, serial analysis, and network analysis. Topic modeling, time series analysis, and network analysis were used to analyze specific topics, trends, and structures, respectively. The results were summarized into three sets as follows. First, the specific topics of scholarly communication research were nineteen in number, including research resource management and research data, and their research proportion is even. Second, as a result of the time series analysis, there are three upward trending topics: Topic 6: Open Access Publishing, Topic 7: Green Open Access, Topic 19: Informal Communication, and two downward trending topics: Topic 11: Researcher Network and Topic 12: Electronic Journal . Third, the network analysis results indicated that high mean profile association topics were related to the institution, and topics with high triangle betweenness centrality, such as Topic 14: Research Resource Management, shared the citation context. Also, through cluster analysis using parallel nearest neighbor clustering, six clusters connected with different concepts were identified.



Abstract
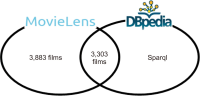
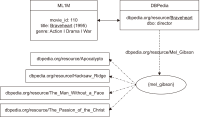
Recommender Systems have gained immense popularity due to their capability of dealing with a massive amount of information in various domains. They are considered information filtering systems that make predictions or recommendations to users based on their interests and preferences. The more recent technology, Linked Open Data (LOD), has been introduced, and a vast amount of Resource Description Framework data have been published in freely accessible datasets. These datasets are connected to form the so-called LOD cloud. The need for semantic data representation has been identified as one of the next challenges in Recommender Systems. In a LOD-enabled recommendation framework where domain awareness plays a key role, the semantic information provided in the LOD can be exploited. However, dealing with a big chunk of the data from the LOD cloud and its integration with any domain datasets remains a challenge due to various issues, such as resource constraints and broken links. This paper presents the challenges of interconnecting and extracting the DBpedia data with the MovieLens 1 Million dataset. This study demonstrates how LOD can be a vital yet rich source of content knowledge that helps recommender systems address the issues of data sparsity and insufficient content analysis. Based on the challenges, we proposed a few alternatives and solutions to some of the challenges.






Abstract
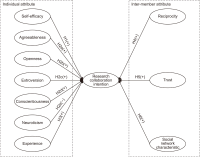
Research collaboration is an important strategy to improve research output, and virtual academic communities (VACs) have become an important platform to collaborate on. This paper reveals the influencing factors of researchers’ collaboration intention in VACs from two attributes: individual, and inter-members. On the basis of the Social Cognitive Theory, Social Exchange Theory, social network theory, and Five-Factor Model, this paper constructed a model demonstrating the influencing factors of VACs researchers’ collaboration intention. A self-administered questionnaire was employed on members of four VACs in China to collect data; subsequently, 558 usable responses were analyzed using structural equation modeling. The result showed that openness, conscientiousness, reciprocity, trust, and the social network characteristic had a significant influence on the collaboration intention of researchers in VACs, while self-efficacy, agreeableness, extroversion, neuroticism, and experience had no significant effects on the collaboration intention of researchers in VACs. This model plays a positive role in promoting the research collaboration intention of Chinese VACs researchers and in guiding the construction of VAC platforms.