JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE THEORY AND PRACTICE
- P-ISSN2287-9099
- E-ISSN2287-4577
- SCOPUS, KCI
12권 1호
초록
Abstract
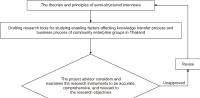
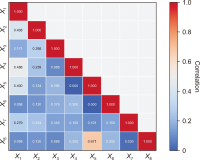
This research aims to study and confirm enabling factors affecting the knowledge transfer and business process of community enterprise groups in Pattani province, Thailand. Key informants were community enterprise entrepreneurs; 30 people were selected purposively with criteria. This study used a mixed-methods approach and conducted semi-structured interviews to collect data. Qualitative data were analyzed using content analysis and classification, while quantitative data were analyzed using descriptive statistics with frequency, percentage, mean, and standard deviation. Moreover, inferential statistics chi-square value, Phi Cramer’s V, and multiple regression analysis with the R program for statistical computing were employed to analyze the relationship between the variables, test the research hypothesis, and create forecasting equations. The research results revealed that the overview of enabling factors had a very high relationship (Cramer’s V=0.965). Regarding community enterprise, it was found that enabling factors related to the knowledge transfer and business process consisted of four factors: regulations and administrative guidelines, business plan, reinforcement, and brainstorming. Reinforcement was the factor with the highest degree of correlation (Cramer’s V=0.873) and predictor of influence on the knowledge transfer and business process (R2=0.670, p<0.05). This study’s findings can lead to the developing of guidelines for promoting community enterprises properly and timely. These guidelines are expected to be used to develop knowledge about business models for community enterprises, which will help to improve their competency and competitiveness.

초록
Abstract
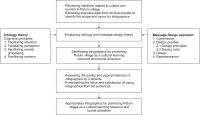
Infographics are influential and valuable communication tools for providing information, and can be used for promoting cultural learning resources and cultural tourism destinations. Therefore, this article presents values of using infographics for promoting Patum’s culture and tourism in Phrao District, Chiang Mai, Thailand as cultural learning resources and tourist attractions. Employing a research and development approach, this study utilized three distinct instruments: (1) an interview form engaging 40 locals to uncover insights on promoting Patum village, (2) an assessment form evaluated by three arts and design experts, and (3) questionnaires distributed to 92 participants to gauge perceptions and satisfaction. The findings showcased the high quality and appropriateness of the eight infographics. Audiences derived six key values, including acquiring knowledge, fostering the promotion of Patum’s culture, festivals, religions and beliefs, deriving aesthetic enjoyment, encouraging cultural tourism, contributing to the education sector, and enhancing comprehension of Patum’s history. Participants expressed high satisfaction (x̅=4.46) with the infographic use. The developed infographics are usable and valuable information to help audiences recognize Patum cultural learning resources and tourist destinations. They might be further tailored to the recognition of Patum village in the near future, affecting the area’s development by increasing local people’s incomes through cultural learning resources and tourism activities.




초록
Abstract
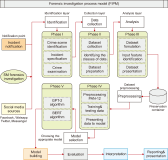
An online social network is a platform that is continuously expanding, which enables groups of people to share their views and communicate with one another using the Internet. The social relations among members of the public are significantly improved because of this gesture. Despite these advantages and opportunities, criminals are continuing to broaden their attempts to exploit people by making use of techniques and approaches designed to undermine and exploit their victims for criminal activities. The field of digital forensics, on the other hand, has made significant progress in reducing the impact of this risk. Even though most of these digital forensic investigation techniques are carried out manually, most of these methods are not usually appropriate for use with online social networks due to their complexity, growth in data volumes, and technical issues that are present in these environments. In both civil and criminal cases, including sexual harassment, intellectual property theft, cyberstalking, online terrorism, and cyberbullying, forensic investigations on social media platforms have become more crucial. This study explores the use of machine learning techniques for addressing criminal incidents on social media platforms, particularly during forensic investigations. In addition, it outlines some of the difficulties encountered by forensic investigators while investigating crimes on social networking sites.



초록
Abstract
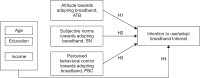
Broadband Internet has proven to be vital for economic growth in developed countries. Developing countries have implemented several initiatives to increase their broadband access. However, its full potential can only be realized through adoption and use. With lower-middle-income countries accounting for the majority of the world’s unconnected population, this study employs the theory of planned behavior (TPB) to investigate users’ intentions to adopt broadband. Rural Tanzania was chosen as a case study. A cross-sectional study was conducted over three weeks, using 155 people from seven villages with the lowest broadband adoption rates. Non-probability voluntary response sampling was used to recruit the participants. Using the TPB constructs: attitude toward behavior (ATB), subjective norms (SN), and perceived behavioral control (PBC), ordinal regression analysis was employed to predict intention. Descriptive statistical analysis yielded mean scores (standard deviation) as 3.59 (0.46) for ATB, 3.34 (0.40) for SN, 3.75 (0.29) for PBC, and 4.12 (0.66) for intention. The model adequately described the data based on a comparison of the model with predictors and the null model, which revealed a substantial improvement in fit (p<0.05). Moreover, the predictors accounted for 50.3% of the variation in the intention to use broadband Internet, demonstrating the predictive power of the TPB constructs. Furthermore, the TPB constructs were all significant positive predictors of intention: ATB (β=1.938, p<0.05), SN (β=2.144, p<0.05), and PBC (β=1.437, p=0.013). The findings of this study provide insight into how behavioral factors influence the likelihood of individuals adopting broadband Internet and could guide interventions through policies meant to promote broadband adoption.




초록
Abstract
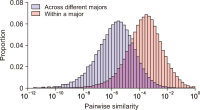
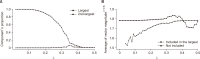
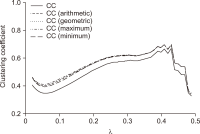
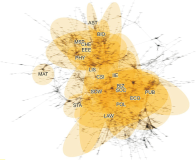
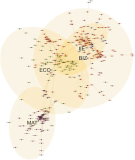
As the significance of knowledge convergence continues to grow, universities are making efforts to develop methods that promote multidisciplinary learning. To address this educational challenge, our paper applies network theory and text mining techniques to analyze university curricula and introduces a graphical syllabus rendering method. Visualizing the course curriculum provides a macro and structured perspective for individuals seeking alternative educational pathways within the existing system. By visualizing the relationships among courses, students can explore different combinations of courses with comprehensive search support. To illustrate our approach, we conduct a detailed demonstration using the syllabus database of Yonsei University. Through the application of our methods, we create visual course networks that reveal the underlying structure of the university curriculum. Our results yield insights into the interconnectedness of courses across various academic majors at Yonsei University. We present both macro visualizations, covering 18 academic majors, and visualizations for a few selected majors. Our analysis using Yonsei University’s database not only showcases the value of our methodology but also serves as a practical example of how our approach can facilitate multidisciplinary learning.




초록
Abstract
As the academic publishing environment evolves rapidly and the open science paradigm emerges, the demand for efficient and transparent peer review is growing. This study outlines efforts to actively introduce advanced concepts in scholarly communication into the submission and review system. AccessON Peer Review Management System Plus (ACOMS+), developed and operated by the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information, is an online submission and peer review system that aims for open science. This study provides an overview of ACOMS+ and presents its four main features: open peer review, open access publishing and self-archiving, online quantitative/qualitative evaluation, and peer reviewer invitation. The directions for further developing ACOMS+ to fully support open science are also discussed. ACOMS+ is the first system in Korea to introduce the open peer review process and is distinguished as a system that supports open access publishing and digital transformation of academic journals. Furthermore, ACOMS+ is expected to contribute to the advancement of the academic publishing environment through the increasing shift toward open access publishing, transparent peer review, and open science.