Vol.10 No.3
Abstract
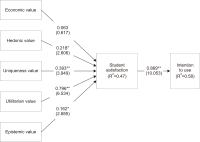
The present study investigates the impact of perceived value metrics in driving satisfaction and behavioral intention to use e-resource among its users. Utilitarian, hedonic, uniqueness, epistemic, and economic are key values selected for the purpose of investigation in the study. This empirical study is carried out through a survey and responses have been analyzed using structural equation modelling. The target group is selected by means of simple random sampling (users of e-resources in selected business schools). Findings of the study reveal that utilitarian values, hedonic values, epistemic values, and uniqueness values have a significant impact on the usage intention of e-resources; however, economic values reflect an insignificant relationship to intention to use e-resources. The study is a distinctive piece of work on investigating the most and the least significant value(s) associated with satisfaction and usage intentions of e-resources.


Abstract
Participants in real-time online sessions, be it (business) meetings, virtual school lessons, or social live streams, all engage in cyber social interactions. Unlike parasocial interactions, cyber social interactions are characterized by reciprocity and temporal proximity. In contrast to social interactions, they lack spatial proximity and bodily contact. This is a fairly new concept in information science that rose from technological advances and unprecedented circumstances (e.g., the rise of digital economy and knowledge workers being able to work remotely or, more recently, global lockdowns and contact restrictions). As a result, the past ways of working and socializing were transformed by making them, in some cases predominantly, virtual. Regarding the example of social live streaming we exhibit the importance of cyber social interactions for information behavior research. This conceptual article is a plea for information science to engage more in human-human online relations and interactions.


Abstract
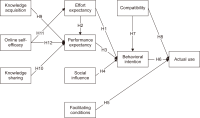
Online learning is becoming ubiquitous worldwide because of its accessibility anytime and from anywhere. However, it cannot be successfully implemented without understanding constructs that may affect its adoption. Unlike previous literature, this research extends the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology with three well-known theories, namely compatibility, online self-efficacy, and knowledge sharing and acquisition to examine online learning adoption. A total of 264 higher education students took part in this research. Partial Least Squares-Structural Equation Modeling was used to evaluate the proposed theoretical model. The findings suggested that performance expectancy and compatibility were significant predictors of behavioral intention, whereas behavioral intention, facilitating conditions, and compatibility had a significant and direct effect on online learning’s actual use. The results also showed that knowledge acquisition, knowledge sharing, and online self-efficacy were determinates of performance expectancy. Finally, online self-efficacy was a predictor of effort expectancy. The proposed model achieved a high fit and explained 47.7%, 75.1%, 76.1%, and 71.8% of the variance of effort expectancy, performance expectancy, behavioral intention, and online learning actual use, respectively. This study has many theoretical and practical implications that have been discussed for further research.


Abstract
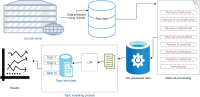
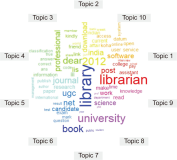
This paper aims to implement a topic modeling technique for extracting the topics of online discussions among library professionals in India. Topic modeling is the established text mining technique popularly used for modeling text data from Twitter, Facebook, Yelp, and other social media platforms. The present study modeled the online discussions of Library and Information Science (LIS) professionals posted on Lis Links. The text data of these posts was extracted using a program written in R using the package “rvest.” The data was pre-processed to remove blank posts, posts having text in non-English fonts, punctuation, URLs, emails, etc. Topic modeling with the Latent Dirichlet Allocation algorithm was applied to the pre-processed corpus to identify each topic associated with the posts. The frequency analysis of the occurrence of words in the text corpus was calculated. The results found that the most frequent words included: library, information, university, librarian, book, professional, science, research, paper, question, answer, and management. This shows that the LIS professionals actively discussed exams, research, and library operations on the forum of Lis Links. The study categorized the online discussions on Lis Links into ten topics, i.e. “LIS Recruitment,” “LIS Issues,” “Other Discussion,” “LIS Education,” “LIS Research,” “LIS Exams,” “General Information related to Library,” “LIS Admission,” “Library and Professional Activities,” and “Information Communication Technology (ICT).” It was found that the majority of the posts belonged to “LIS Exam,” followed by “Other Discussions” and “General Information related to the Library.”






Abstract
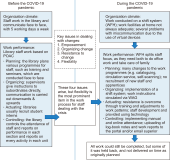
This study aims to understand human resource management in the Library of the House of Representatives of the Republic of Indonesia (DPR RI) during the COVID-19 pandemic. This institution had to change its work procedures, including its management of human resources. The research uses a qualitative approach with a case study method. Data was collected through interviews, observations, and document analysis, carried out from October to December 2020. The findings show that working from home practices had the following impacts: reduced ability to concentrate while working; many forced changes to the work programme; and problems of miscommunication due to work instructions being conveyed through a WhatsApp group. In response to the situation, the planning function of management was used to suspend the recruitment of interns; the organizing function was divided up tasks into two or three working days a week; the actuating function was seen in the willingness of leadership to motivate staff and to optimize resources by providing training; and the controlling function was realized in an online presence and online reporting mechanisms. It was concluded that the implementation of human resource management in the library was achieved through flexibility and staff empowerment. This involved carrying out initiatives and controlling their effectiveness in response to whatever changes were required by the latest pronouncements from government. Obstacles were still encountered in the implementation of these changes, especially in relation to the organizing function of management, where some conflict was seen between the DPR RI librarians.

Abstract
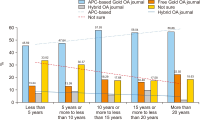
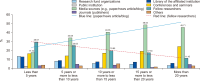
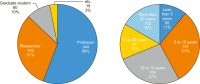
This study aims to determine the awareness and perceptions of Korean researchers regarding mandatory open access (OA) and OA publishing of publicly-funded research papers. In July 2019, Korean researchers who had published in Science Citation Index Expanded journals as first authors and corresponding authors participated in an online survey distributed via e-mail. A total of 1,172 valid responses were collected and analyzed using SPSS 18. The results indicated that the level of awareness of OA differed significantly based on occupation and research experience (p<0.001). Although 52.56% of the respondents had experienced OA publishing, only 22.35% had self-archiving experience. Regardless of the amount of publishing cost support, researchers showed a high level of willingness to publish OA articles. Yet, since the importance of impact factor was evaluated to be very high, at present OA publication might have a limited role as a publication platform.