ISSN : 2287-9099
Vol.5 No.3
Abstract
Workplace knowledge sharing is a complex process and there are a large number of studies in the area. In this article three theoretical approaches in library and information science are used to discuss knowledge sharing in the workplace. The approaches are information behavior, social capital, and information culture, and they bring important insights that need to be considered from a holistic management point of view when it comes to knowledge sharing. The individual’s relation to different levels of context is important, meaning both in relation to work roles, work tasks, situations, organizational structures, and culture. The frameworks also shed light on where and how knowledge sharing activities are present in the organization. From a knowledge management point of view, it is important to acknowledge that when knowledge is valued, there is also an awareness of the knowledge sharing activities. Also, in addition to more traditional views of context, the frameworks bring forward different views on context, such as time and space as contextual factors.
Abstract
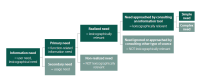
In some situations, you need information in order to solve a problem that has occurred. In information science, user needs are often described through very specific examples rather than through a classification of situation types in which information needs occur. Furthermore, information science often describes general human needs, typically with a reference to Maslow’s classification of needs (1954), instead of actual information needs. Lexicography has also focused on information needs, but has developed a more abstract classification of types of information needs, though (until more recent research into lexicographical functions) with a particular interest in linguistic uncertainties and the lack of knowledge and skills in relation to one or several languages. In this article, we suggest a classification of information needs in which a tripartition has been made according to the different types of situations: communicative needs, cognitive needs, and operative needs. This is a classification that is relevant and useful in general in our modern information society and therefore also relevant for information science, including lexicography.

Abstract
The narrow-down approach, separately composed of search and classification stages, is an effective way of dealing with large-scale hierarchical text classification. Recent approaches introduce methods of incorporating global, local, and path information extracted from web taxonomies in the classification stage. Meanwhile, in the case of utilizing path information, there have been few efforts to address existing limitations and develop more sophisticated methods. In this paper, we propose an expansion method to effectively exploit category path information based on the observation that the existing method is exposed to a term mismatch problem and low discrimination power due to insufficient path information. The key idea of our method is to utilize relevant information not presented on category paths by adding more useful words. We evaluate the effectiveness of our method on state-of-the art narrow-down methods and report the results with in-depth analysis.
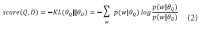
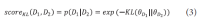
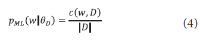
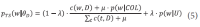
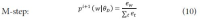
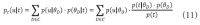
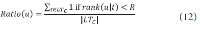
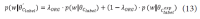
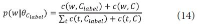
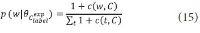

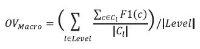

Abstract
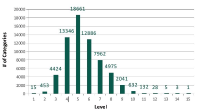
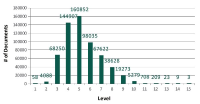
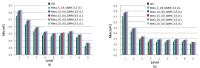
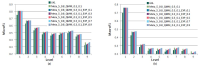
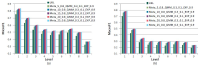
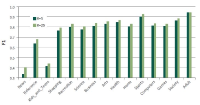
The purpose of this paper is to understand the profiles of users and their motivations in sharing research articles on Twitter. The goal is to contribute to the understanding of Twitter as a new altmetric measure for assessing impact of research articles. In this paper, we extended the previous study of tweet motivations by finding out the profiles of twitter users. In particular, we examined six characteristics of users: gender, geographic distribution, academic, non-academic, individual, and organization. Out of several, we would like to highlight here three key findings. First, a great majority of users (86%) were from North America and Europe indicating the possibility that, if in general, tweets for research articles are mainly in English, Twitter as an alternative metric has a Western bias. Second, several previous altmetrics studies suggested that tweets, and altmetrics in general, do not indicate scholarly impact due to their low correlation with citation counts. This study provides further details in this aspect by revealing that most tweets (77%) were by individual users, 67% of whom were nonacademic. Therefore, tweets mostly reflect impact of research articles on the general public, rather than on academia. Finally, analysis from profiles and motivations showed that the majority of tweets (from 42% to 57%) in all user types highlighted the summary or findings of the article indicating that tweets are a new way of communicating research findings.
Abstract
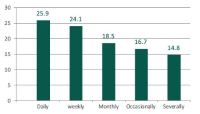
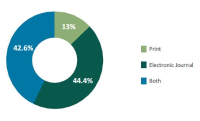
This study investigated the use of e-journals by health researchers in the Nigerian Institute of Medical Research (NIMR). A descriptive survey method was adopted for the study and a questionnaire was used for data collection. The study population was comprised of fifty-four (54) respondents who are health researchers in the institute. The data collected were presented and analyzed using tables, frequency distribution, simple percentages, and charts. The result of the study revealed that all the respondents are aware of the availability of e-journals and attest to making use of them. The study revealed that electronic journals were mostly used for the purpose of conducting research work and the PDF format was preferred for downloading e-journals. However, it was observed that low Internet connectivity and intermittent electricity supply constitute a major obstacle to the use of e-journals. The study, therefore, recommended that the institute’s management invest more resources on network connectivity, particularly its bandwidth, and ensure reliable power supply.