ISSN : 2287-9099
Vol.5 No.2

Abstract
Populating information-rich online environments through crowdsourcing is increasingly becoming popular. One approach to motivate participation is via games. That is, a crowdsourcing game offers entertainment while generating useful outputs as byproducts of gameplay. A gap in current research is that actual usage patterns of crowdsourcing games has not been investigated thoroughly. We thus compare content creation patterns in a game for crowdsourcing mobile content against a non-game version. Our analysis of 3323 contributions in both apps reveal 10 categories including those that conform to the traditional notion of mobile content created to describe locations of interest, and those that are social in nature. We contend that both types of content are potentially useful as they meet different needs. Further, the distribution of categories varied across the apps suggesting that games shape behavior differently from non-game-based approaches to crowdsourcing.



Abstract
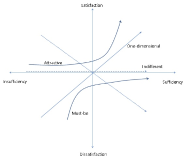
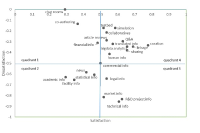
We compared nanotechnology web portal requirements using a Kano method, to identify similarities and dissimilarities in Kano-categorizations of features and functions required of nanotechnology among users in universities, government research institutes, and industry. Based upon data obtained from 130 user members of the National Nanotechnology Policy Centre, this study analyzed assessed asymmetries in web users’ feelings based on hypothesized provision and non-provision of web portal requirements. In doing this, this study utilized measures and procedures suggested in the literature such as the most frequent-response categorization, customer satisfaction (dissatisfaction) coefficient, category strength and total strength, and Fong test. This study found that overall, sectors were an important factor in explaining the relationships between web portal requirements and user satisfaction/expectations. When these requirements were classified, users’ perceptions of information contents requirements were consistent across the sectors, but the other functional requirements including communication and collaborations considerably varied.



Abstract
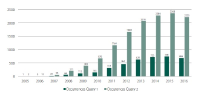
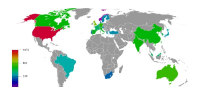
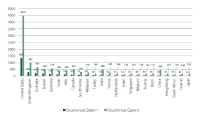
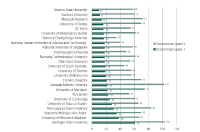
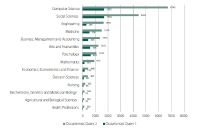
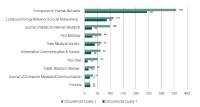
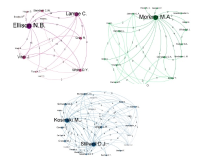
The aim of the present study is to analyze the present state and evolution of scientific research with regard to the scientific production generated on Facebook. Good analysis proves challenging due to the large number of publications about the topic. That is why we concentrate on Scopus as the information service with the highest coverage on this topic. We performed a bibliometric analysis on Facebook-related research from 2005 to 2016. We identified publication output, subject areas, journals, and countries in order to assess the publication trends and research hotspots in this field. Moreover, an author network graph and a geo map were applied to visualize some research trends. These results provide a basis for better understanding of the development of global Facebook research.



Abstract
This paper uses 601 cited papers of Pakistani LIS researchers with the purpose to examine the individual performance of these Library and Information Science (LIS) researchers in terms of their research output and its impact on the LIS (national/international) literature by using various bibliometric indicators. A list of 139 authors was compiled with the help of the Library, Information Science, and Technology Abstracts (LISTA) and some other sources. Data were collected from Google Scholar and SPSS version 20 was utilized in order to identify the relationship between self-citations and various performance indices of the authors. The average citations received per paper vary from 1.80 to 10.08. About half of the papers were single-authored whereas less than one-fifth were by three or more authors. The authors who worked in collaboration produced more papers and received more citations. The h-index, g-index, hI-index, hI-norm, and e-index were used to determine the rank for each author. The intra-group citations grid revealed the volume of self-citations and a small group who cite each other more due to close academic and social relationships. The correlations between self-citations and the impact indices used revealed significant differences. Findings are useful for concerned institutions regarding award, promotions, etc. Further, future research should seriously consider the self-citations and social networking of authors while examining their citations-based research performance.
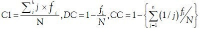
Abstract
This study examined the mechanical engineering research output from India, Japan, and South Korea on different parameters including growth, collaboration indices, and activity index. The purpose of the study is to understand the overall development of mechanical engineering through analytical approaches applied on the scholarly outcome of the countries considered for the study. The study focuses on analysing the articles published by India, Japan, and South Korea, and is restricted to articles indexed in the Science Citation Index – Web of Science for the period 2000 to 2014. The ratios of number of paper to citations for India, Japan, and Korea are 20,836: 1,97,679; 24,494: 2,04,393; and 30,578: 2,66,902 respectively for the period 2000-2014. The findings show that there is a decline in Japanese publications in mechanical engineering, whereas other two countries have recorded an increasing trend. While India has tripled its publications in a span of 15 years, South Korea, on the other hand, has doubled its publications in the same span of time. There has been an increasing trend towards collaboration in almost all fields of science and technology. However, the extent of collaboration and their rate of growth varied for one subject to another, one branch to another branch of the same subject, and from one country to another country. The present study analyses the growth of research publications of the mechanical engineering domain including authorship distribution, collaboration indices, prominent journals, and activity index.