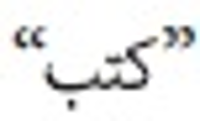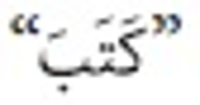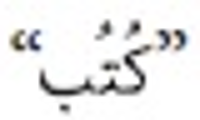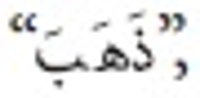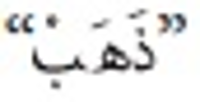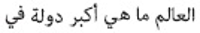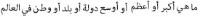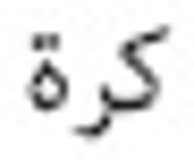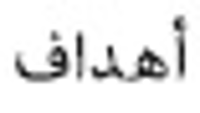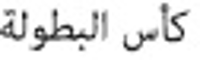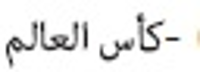Vol.8 No.4
Abstract
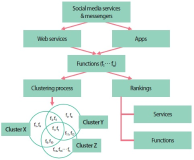
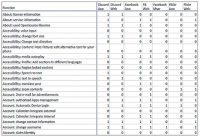
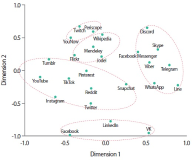
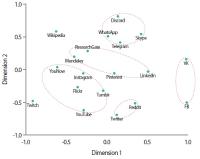
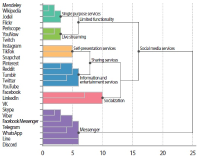
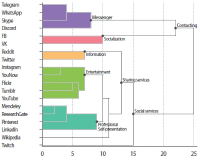
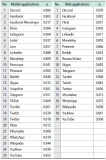
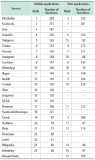
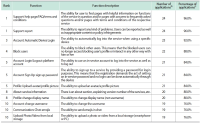
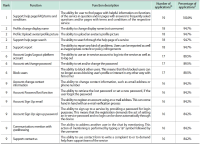
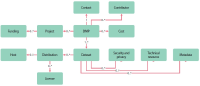
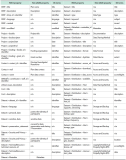
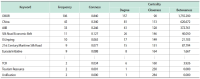
The objective of this research is to analyze which functions make up web-based as well as mobile social media services and messengers. Services are clustered by their functionality. A total of 640 individual functions were identified, while investigating altogether 44 selected services in their web and mobile versions. Applying content analysis, functions were assigned to the services. The services were ranked by the number of implemented functions, and the functions were ranked by their occurrence in the services. Cluster analysis was applied to classify the services according to their functionality. Facebook and VKontakte were found to be the ones with the most functions; the most frequently implemented functions are support, profile, and account-related. Cluster analysis revealed six classes for mobile and seven classes for web applications. There is a noteworthy difference regarding the functionality scope between web and mobile applications of the same services. An example for this is Mendeley with 38 functions in the mobile and 91 functions in the web version. This is the first empirical attempt at clustering social media services based on their functionality.

Abstract
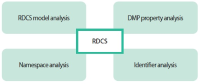
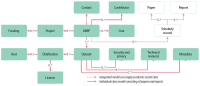
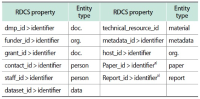
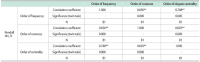
In this study, the RDA DMP Common Standard (RDCS), a data model for implementing a machine actionable Data Management Plan (maDMP), was analyzed in four aspects. First, the twelve class models proposed by RDCS were analyzed. Second, whether the DMP attribute was included in the class attribute was analyzed. Third, we analyzed the namespace used for RDCS properties. Fourth, the values and identifiers used in RDCS properties were analyzed. As a result of the analysis, four directions for improvement were derived. First, it is necessary to add an academic record class to describe information such as papers and reports, which are representative academic documents. Second, the primary research institution, responsibility, resources, option attribute, and additional attributes are needed to describe the researcher’s affiliation information. Third, it is necessary to additionally use a namespace such as Friend of a Friend that can be used universally. Fourth, the use of digital object identifier should be considered to identify academic literature.

Abstract
The diverse set of phenomena, concepts, and activities existing in academic disciplines could be studied from multiple perspectives. One of the promising approaches to explore phenomena is hermeneutics, especially in the form of hermeneutic phenomenology, which has been formed as a consequence of postmodern movements. Hermeneutic phenomenology has taken root in the original ideas of philosophers like Husserl, Heidegger, and Gadamer, and has become one of the fruitful research methodologies over time. After a brief review of the foundations of hermeneutic and phenomenological methodologies, the role of the hermeneutic phenomenology approach in supporting research and information services is discussed. The present article seeks to describe narratively the use of hermeneutic phenomenology in such issues as information technology, information behavior, knowledge organization, and librarians’ roles as related to Information Science.

Abstract
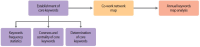
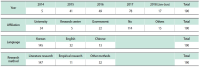
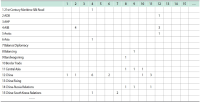
This proposed work aims to understand the Korean Academic Circle (KAC)’s research trend on the “One Belt One Road” (OBOR) by employing a quantitative analysis of the recent research articles published by the KAC. To do so, this proposed research has used the well-known network analysis software, Ucinet 6, by which the papers on related topics are collected and filtered from Korea Citation Index. To perform the analytical selection, the proposed work has chosen ‘keywords’ as the core research object and performed analysis from transverse to longitudinal aspects, and from holistic to individual aspects, respectively; and from this, the KAC’s research trend on OBOR is derived. The present work has established that the KAC’s attention is continuously increasing on OBOR and has sustainability. Centered on the OBOR, Korean researchers have spread their studies in various dimensions ranging from the issues like China’s political economy to Sino-Korea economic and trade exchanges, and so on. The KAC has even combined OBOR with Korea’s international development initiatives, which can help Korea benefit from active and sustainable cooperation with China. Moreover, the proposed work has found that Korean researchers have also actively expressed their growing attention, highlighted Korea’s interest, and showed concern about China hegemony and Sinocentrism in their recent documented research works.




Abstract
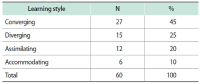
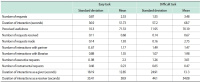
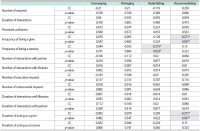
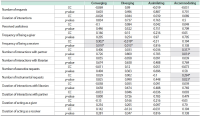
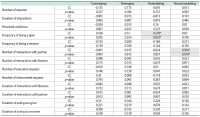
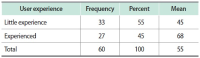
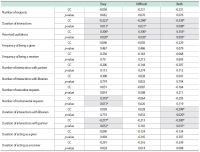
The purpose of this study is to examine the relationship between collaborative information seeking and users’ learning style preferences and their experience of information systems. The study investigates the role of four different factors including learning style, task complexity, and user experience in collaborative information seeking in digital environments. Sixty participants (30 pairs) were randomly chosen from volunteer graduate students of Kharazmi University (Iran). Participants completed Kolb’s learning style questionnaire and a user experience questionnaire and then performed two information seeking tasks (one simple and one difficult) in a lab setting. They could exchange information with their partners or a librarian using Skype. The sessions were recorded using Camtasia. The results showed that with an increase in task difficulty, collaborative information seeking activities increased and more interactions with partners and the librarian occurred. The number of executive help-seeking requests was higher than the number of instrumental help-seeking requests. This research confirms that learning style is related to the way users interact with the digital library and help seeking. The research showed that in difficult tasks, the differences among users with different learning styles become more evident, and that generally interactions increase in more difficult tasks. Among the learning styles, the accommodating style had the highest number of relationships with collaborative information seeking variables. Most of the statistically significant relationships between users’ prior computer experience and collaborative information seeking variables were related to the time variable.


Abstract
Information need has been one of the main motivations for a person using a search engine. Queries can represent very different information needs. Ironically, a query can be a poor representation of the information need because the user can find it difficult to express the information need. Query Expansion (QE) is being popularly used to address this limitation. While QE can be considered as a language-independent technique, recent findings have shown that in certain cases, language plays an important role. Arabic is a language with a particularly large vocabulary rich in words with synonymous shades of meaning and has high morphological complexity. This paper, therefore, provides a review on QE for Arabic information retrieval, the intention being to identify the recent state-of-the-art of this burgeoning area. In this review, we primarily discuss statistical QE approaches that include document analysis, search, browse log analyses, and web knowledge analyses, in addition to the semantic QE approaches, which use semantic knowledge structures to extract meaningful word relationships. Finally, our conclusion is that QE regarding the Arabic language is subjected to additional investigation and research due to the intricate nature of this language.