Vol.12 No.2
Abstract
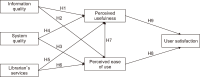
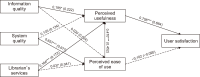
This study aims to develop a comprehensive technological framework anchored in a theoretical model to assess user satisfaction with university library websites (ULWs) in Myanmar. Adopting a quantitative approach, data were obtained via convenience sampling and subsequent inferential analysis. The target population for this study investigated users of various ULWs in Myanmar who were utilizing six university libraries. Of the collected responses, 273 valid surveys were analyzed using SPSS (version 25) and AMOS. Tools such as structural equation modeling and confirmatory factor analysis played pivotal roles in data interpretation and hypothesis validation. The proposed model highlights the significance of information quality, system quality, and librarian services in influencing both perceived usefulness (PU) and perceived ease of use (PEOU), culminating in user satisfaction. Notably, information quality and librarian services primarily impact PU, while system quality is more influential on PEOU. Interestingly, while PU has a direct bearing on user satisfaction, PEOU does not. Moreover, demographic elements such as age, gender, and education level introduce considerable differences in the utilization of ULW services. Drawing from the study’s findings, recommendations are made for ULW managers in Myanmar to bolster services, aligning with user preferences. The resulting framework offers tangible benefits to Myanmar’s educational sector, including academia, government entities, librarians, and policy framers. This pioneering research delves into the realm of ULWs in Myanmar’s higher education sector. Practically, the research underscores the necessity for stakeholders, encompassing Myanmar’s library experts and governing bodies, to elevate the standard of ULWs. Theoretically, a salient takeaway is the direct linkage between heightened usefulness and increased user satisfaction.

Abstract
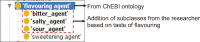
There has been a growing interest in halal-related ontology research in recent years, as ontology has gained recognition in the halal industry. This paper discusses the development of a flavouring ontology that will assist halal management auditors in predicting the halal status of flavours in order to process food producers’ applications for halal certification. The development of a flavouring ontology is based on multiple references, because the auditors of halal management divisions must consult a variety of sources independently in order to determine the halal status of flavourings. The process includes 1) determining the ontology goal and scope, 2) building ontologies, and 3) evaluating the ontologies. The researcher used Protégé to design the ontologies, and Phyton was used to develop a prototype based on flavouring ontology. The developed ontology consists of four classes, nine sub-classes, and 11 relationships. The evaluation of the ontology using the prototype revealed that the majority of experts were satisfied with the information generated by the ontology in the prototype, particularly in relation to synonyms and the hierarchical structure of a flavour. However, the experts suggest improvements in terms of flavour metadata, especially on raw materials and natural occurrence data, so that the flavour information retrieved is comprehensive and accurate.



Abstract
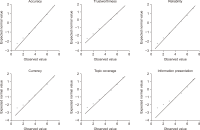
For consumers making health decisions, Wikipedia is a popular source for health information. This study investigated major factors influencing consumer satisfaction with Wikipedia medical/health articles. Using a crowdsourcing method, data were collected from 322 adults who read/edit English Wikipedia medical/health articles and reside in the US. The results showed that the presentation of information was the most influential factor. Trustworthiness was the second most important factor for consumer satisfaction with the quality of information, followed by reliability, and topic coverage. Study participants did not consider other factors such as accuracy and currency to be crucial factors. Moderating effects of the control variables such as editing experience with Wikipedia articles, gender, and age were also examined to enhance the internal validity of the study. Implications for the Wikipedia editor community and researchers, and directions of future research are presented.

Abstract
Information behavior played a significant role in minimizing the risks of the COVID-19 pandemic. When faced with such a situation, an individual needs information for decision-making and in order to determine the best course of action relating to their health. This study aims to explore information behavior during each phase of the COVID-19 pandemic in Indonesia, which is known for its close-knit collective culture. A sensemaking approach is used, which emphasizes the process individuals go through to understand their situation and give meaning to the information they are getting from their environment. Data was collected through in-depth interviews with 10 participants to obtain a description of their information behaviors during the pandemic. Data analysis was carried out using open, axial, and selective coding. We propose a sensemaking-based information behavior strategy framework for mitigating risk and reducing ongoing health crises. Changes in information behavior strategies, including search, prevention, and restriction of information exposure, were random at the beginning of the pandemic, but became more regular in later phases. This was influenced by the “knowledge gap fulfillment” and “use of local knowledge” among the participants throughout the pandemic. In conclusion, the participants developed a sensemaking process including an understanding of the pandemic situation and the risks that they faced. They used a number of information behavior strategies to prevent transmission, and their perception of the risks changed across the course of the pandemic, up til the situation began to be considered back to normal again in Indonesia.
Abstract
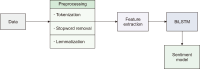
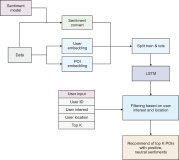
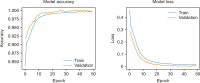
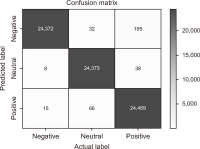
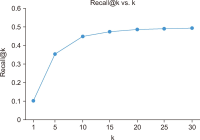
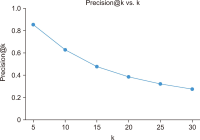
Sentiment analysis is one of the promising approaches for developing a point of interest (POI) recommendation system. It uses natural language processing techniques that deploy expert insights from user-generated content such as reviews and feedback. By applying sentiment polarities (positive, negative, or neutral) associated with each POI, the recommendation system can suggest the most suitable POIs for specific users. The proposed study combines two models for POI recommendation. The first model uses bidirectional long short-term memory (BiLSTM) to predict sentiments and is trained on an election dataset. It is observed that the proposed model outperforms existing models in terms of accuracy (99.52%), precision (99.53%), recall (99.51%), and F1-score (99.52%). Then, this model is used on the Foursquare dataset to predict the class labels. Following this, user and POI embeddings are generated. The next model recommends the top POIs and corresponding coordinates to the user using the LSTM model. Filtered user interest and locations are used to recommend POIs from the Foursquare dataset. The results of our proposed model for the POI recommendation system using sentiment analysis are compared to several state-of-the-art approaches and are found quite affirmative regarding recall (48.5%) and precision (85%). The proposed system can be used for trip advice, group recommendations, and interesting place recommendations to specific users.

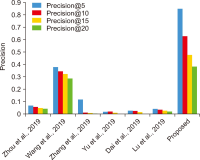
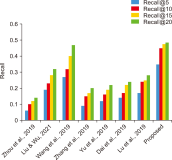

Abstract
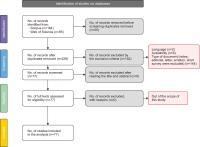
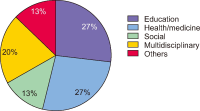
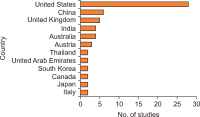
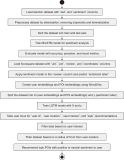
The new AI based conversational chatbot, ChatGPT, launched in November 2022, is causing a stir. There are many opinions about this being a ‘threat or a promise,’ and thus it is important to understand what has been said about this tool and, based on the growing literature that has emerged on the subject, demystify its effective impact on society. To analyse this impact, a systematic literature review with the support of the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis protocol was used. The data, scientific documents, were collected using the main scientific databases – SCOPUS and Web of Science – and the results were presented based on a bibliometric and thematic exploration of content. The main findings indicate that people are increasingly using this chatbot in more diverse areas. Therefore, this study contributes at the practical level, aiming to enlighten people in general – both in professional and personal life – about this tool and its impacts. Also, it contributes at the theoretical level, which involves expanding understanding and elucidation of the impacts of ChatGPT in different areas of study.