Latest Articles
Vol.13 No.1
6papers in this issue.
Abstract
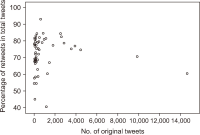
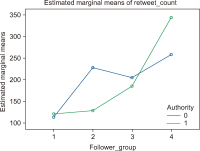
This study aims to investigate whether the prevalence of retweets challenges the validity of Twitter mentions (tweet counts and tweeter counts) as indicators of research significance. The study first examines whether the tweeting of research papers signifies either the wisdom of crowd effect or herd-like behavior for a dataset of COVID-19 papers from The Lancet. The study then uses the Modality, Agency, Interactivity, and Navigability (MAIN) model to examine the nature of the influence involved in retweeting. The Mann-Whitney U test and multiple linear regression were used. Findings show that there was extensive evidence of herdlike behaviour, rather than the wisdom of crowd effect, in tweeting research papers, challenging the validity of Twitter mentions as indicators of research significance. Credibility heuristic cues of the original tweeters were associated with their retweet rates, suggesting that retweets are more likely influenced by perceptions of the original tweeter’s credibility rather than the quality of research papers.

Abstract
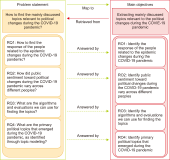
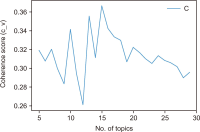
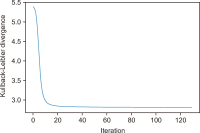
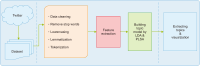
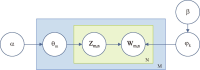
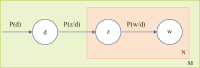
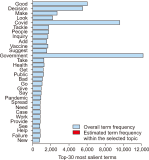
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected various sectors of society, including politics. The political changes have had both positive and negative impacts on people’s lives. Different public discussions happened during that situation on social media. It is essential to understand those discussions to prepare for the same kind of situation in future. Therefore, this study aims to identify the topics discussed on Twitter regarding this influence. During March 2020 and December 2021, 10,658 Tweets were gathered through the Twitter application programming interface and preprocessed using Python libraries. After feature extraction using the bag-ofwords method, both probabilistic latent semantic analysis (PLSA) and latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) were used as topic modeling methods. As a result of the analysis, 15 topics by LDA and 25 topics by PLSA were extracted during the study and then grouped into five key themes: Government responses for managing the COVID-19 Pandemic, Government decisions for COVID-19, Public response to government measures for COVID-19, Social influence, and Vaccination. Through a comparative evaluation of the LDA and PLSA topic modeling techniques, the research identifies LDA as the superior method, providing more accurate and coherent results.






Abstract
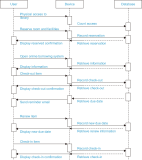
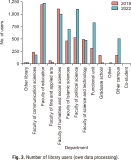
This paper aims to investigate library user behaviors by comparing them pre and post-COVID-19. Two aspects of users’ behaviors were examined, including using physical learning spaces, and online resource utilization. This exploration used secondary data automatically recorded by ALIST OPAC systems (Prince of Songkla University Pattani Campus, Pattani, Thailand) during 2018 and 2022. Descriptive statistics were used to examine physical space usage. The machine learning algorithms name process mining technique was used to investigate the changes in online behaviors, by formulating the sequence of activities based on the digital footprints recorded when users interacted with the systems. This technique exemplified the sequence and timing of activities. The study results revealed an increased use of limited co-learning spaces by library users after COVID-19. The activity of borrowing and returning library resources showed that fewer reminder e-mails on the due date were sent. The process of mining exemplified the sequence and timing of activities. It indicated that after COVID-19, library users hold borrowed items for a shorter time than before the pandemic. These findings suggest that the digital footprints unveiled the changes in library users’ behaviors. That is, the library users return borrowed items faster than in pre-COVID-19 circumstances. A decrease in reminder e-mails was clearly visible to support such a finding. Therefore, it is suggested that library managements should consider a faster operation and well-resourced management to adapt to the changes. Managing resources needs to become faster as the library users showed a potential for faster return of borrowed resources.




Abstract
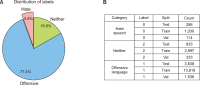
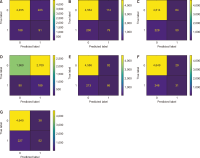
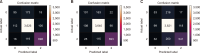
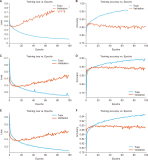
Online social networks empower individuals with limited influence to exert significant control over specific individuals’ lives and exploit the anonymity or social disconnect offered by the Internet to engage in harassment. Women are commonly attacked due to the prevalent existence of sexism in our culture. Efforts to detect misogyny have improved, but its subtle and profound nature makes it challenging to diagnose, indicating that statistical methods may not be enough. This research article explores the use of deep learning techniques for the automatic detection of hate speech against women on Twitter. It offers further insights into the practical issues of automating hate speech detection in social media platforms by utilizing the model’s capacity to grasp linguistic nuances and context. The results highlight the model’s applicability to information science by addressing the expanding need for better retrieval of hazardous content, scalable content moderation, and metadata organization. This work emphasizes content control in the digital ecosystem. The deep learning-based methods discussed improve the retrieval of data connected to hate speech in the context of a digital archive or social media monitoring system, facilitating study in fields including online harassment, policy formation, and social justice campaigning. The findings not only advance the field of natural language processing but also have practical implications for social media platforms, policymakers, and advocacy groups seeking to combat online harassment and foster inclusive digital spaces for women.

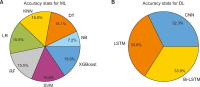
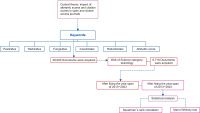
Abstract
This study analyzes the roles of altmetric and citation scores in open and closed-access pesticide research journals from 2013 to 2023, revealing key insights into impact metrics across publishing models. Traditional citations predominantly favor subscriptionbased journals, which account for 68.03% of the total citations. In contrast, green open-access journals excel in altmetric scores, primarily driven by social media engagement on platforms such as Mendeley, Twitter, and Facebook. Green open-access documents record the highest cumulative citations (13,143) and altmetric scores (5,768), suggesting greater online visibility and broader social reach. Statistical analysis shows no significant difference between altmetrics and citations, indicating that both metrics contribute complementary perspectives on research impact. Descriptive statistics highlight variations in citation patterns, with open-access journals showing a more concentrated distribution. Toxicology journals, where much pesticide research is published, are predominantly closed access, though citation patterns and altmetric attention vary by journal. Leading journals such as Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety emphasize citations, while Food and Chemical Toxicology focuses on altmetrics, underscoring the dual approach to research visibility and impact in pesticide studies. These findings emphasize the evolving role of altmetrics in complementing traditional citations, especially for studies with high public and social relevance.


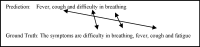
Abstract
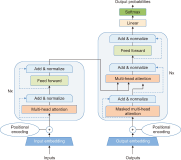
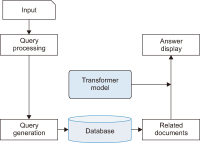
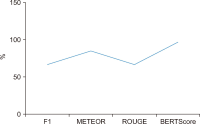
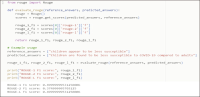
The purpose of this study is to examine how evaluation metrics influence the perception and performance of question answering (QA) systems, particularly focusing on their effectiveness in QA tasks. We compare four different models: BERT, BioBERT, Bio-ClinicalBERT, and RoBERTa, utilizing ten EPIC-QA questions to assess each model’s answer extraction performance. The analysis employs both semantic and lexical metrics. The outcomes reveal clear model-specific behaviors: Bio-ClinicalBERT initially identified irrelevant phrases before focusing on relevant information, whereas BERT and BioBERT continually converge on similar answers, exhibiting a high degree of similarity. RoBERTa, on the other hand, demonstrates effective use of long-range dependencies in text. Semantic metrics outperform lexical metrics, with BERTScore attaining the maximum accuracy (0.97), highlighting the significance of semantic evaluation. Our findings indicate that the choice of evaluation metrics significantly influences the perceived efficacy of models, suggesting that semantic metrics offer more nuanced and insightful assessments of QA system performance. This study contributes to the field of natural language processing and machine learning by providing guidelines for selecting evaluation metrics that align with the strengths and weaknesses of various QA approaches.