JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE THEORY AND PRACTICE
- P-ISSN2287-9099
- E-ISSN2287-4577
- SCOPUS, KCI
7권 4호
초록
Abstract
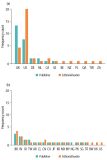
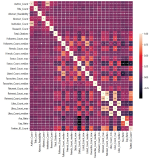
The purpose of this article is to problematize the existence of a possible Ibero-American informational thinking. It was initially observed that a relative absence of Ibero-America in the international presentations and mappings of information science exists. Below, the reality of the 22 countries that compose Ibero-America is discussed, a region that can be understood from a sociocultural and geopolitical perspective. Then, a mapping of the information science research in these countries is made. The main research topics found are: epistemological studies, relationships with library science, information literacy, representation and organization, bibliometric studies, information management, user studies, technological dimensions, and relationships with archival science and museum studies. Finally, a general epistemological configuration of information science is presented at a global level, highlighting the great trends of study of information that marked the decades of the 1960s and 1970s (physical model), 1980s and 1990s (cognitive model), and the 21st century (sociocultural model), and which manifested themselves in the different subareas that make up the field. The most recent research in information science, in addition to addressing information transfer (physical dimension) and its relationship with data and knowledge (cognitive dimension), has also incorporated aspects related to the social effects of information, its role in the constitution of identities and culture, and the importance of its material conformations. Such expansion reflects attempts to address the complexity of informational phenomena. Therefore, it is concluded that it is important to place the specific contributions of Ibero-America in this context.
초록
Abstract
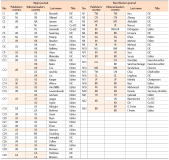
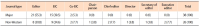
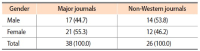
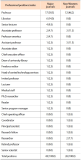
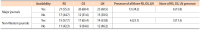
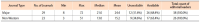
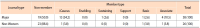
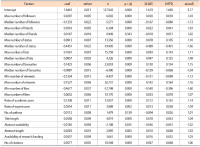
Due to the competitive nature of journal publishing, editorial leadership has become an increasingly important issue on many editorial teams. This study aimed to compare the major and non-Western international journals in library and information science and reveal the differences between them. To conduct this study, journals indexed by Scopus and Web of Science were analyzed in terms of gender, professional position and rank, institutions, and the iSchool status of the editorial leaders’ institutions. The most notable results were the following: a) As a whole, both types of journals lacked true internationalization. Editorial leaders of major journals tended to be from Western countries, whereas editorial leaders of non-Western journals tended to be from non-Western countries; b) Most non-Western journals tended to appoint editorial leaders from the same country as the publisher’s country; and c) Almost all editorial leaders of non-Western journals were from various non-Western countries and tended to have lower h-index scores, and their institutions were not part of the iSchool. Future research should assess editorial leadership, compare the results of this study to other disciplines, and find effective ways to collect data on editorial leaders while minimizing ethical concerns in order to meet future research needs.



초록
Abstract
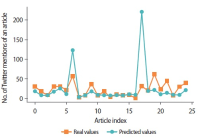
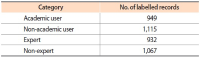
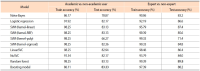
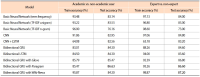
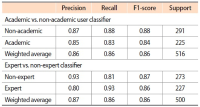
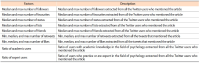
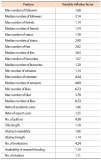
Altmetrics measure the frequency of references about an article on social media platforms, like Twitter. This paper studies a variety of factors that affect the popularity of articles (i.e., the number of article mentions) in the field of psychology on Twitter. Firstly, in this study, we classify Twitter users mentioning research articles as academic versus non-academic users and experts versus non-experts, using a machine learning approach. Then we build a negative binomial regression model with the number of Twitter mentions of an article as a dependant variable, and nine Twitter related factors (the number of followers, number of friends, number of status, number of lists, number of favourites, number of retweets, number of likes, ratio of academic users, and ratio of expert users) and seven article related factors (the number of authors, title length, abstract length, abstract readability, number of institutions, citation count, and availability of research funding) as independent variables. From our findings, if a research article is mentioned by Twitter users with a greater number of friends, status, favourites, and lists, by tweets with a large number of retweets and likes, and largely by Twitter users with academic and expertise knowledge on the field of psychology, the article gains more Twitter mentions. In addition, articles with a greater number of authors, title length, abstract length, and citation count, and articles with research funding get more attention from Twitter users.



초록
Abstract
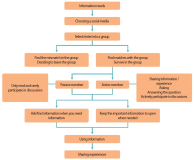
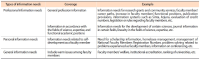
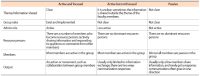
Currently there are many groups of Indonesian faculty members on social media. This research aims to find out the information behavior of Indonesian faculty members on social media, especially on Facebook, Telegram, and WhatsApp. The focus of this research is in-depth understanding of the needs, search, organization, and use of information by Indonesian faculty members on social media. This research is qualitative research using a virtual ethnographic approach. The research data was obtained through participatory observation, in-depth interviews, and a literature review. The selection of informants was done by purposive sampling, while triangulation was done by data sources and theories triangulation. The results showed that the information behavior of Indonesian faculty members on social media began with the need for information, choosing social media, choosing and entering into one or several groups, sharing information, and discussing in a group. Some faculty members keep the information, and some choose to ask when they need the information, even though the information has been discussed. The information obtained is used when they need it, and they usually share their experiences with other group members.


초록
Abstract
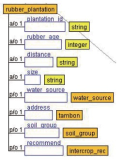
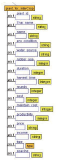
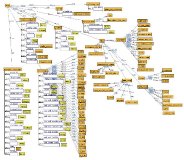
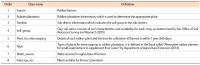
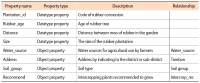
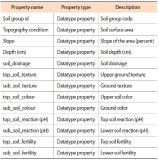
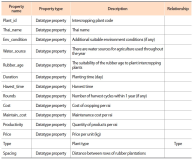
Planting intercropping in rubber plantations is another alternative for generating more income for farmers. However, farmers still lack the knowledge of choosing plants. In addition, information for decision making comes from many sources and is knowledge accumulated by the expert. Therefore, this research aims to create a decision support system for growing rubber trees for individual farmers. It aims to get the highest income and the lowest cost by using semantic web technology so that farmers can access knowledge at all times and reduce the risk of growing crops, and also support the decision supporting system (DSS) to be more intelligent. The integrated intercropping ontology and rule are a part of the decision-making process for selecting plants that is suitable for individual rubber plots. A list of suitable plants is important for decision variables in the allocation of planting areas for each type of plant for multiple purposes. This article presents designing and developing the intercropping ontology for DSS which defines a class based on the principle of intercropping in rubber plantations. It is grouped according to the characteristics and condition of the area of the farmer as a concept of the rubber plantation. It consists of the age of rubber tree, spacing between rows of rubber trees, and water sources for use in agriculture and soil group, including slope, drainage, depth of soil, etc. The use of ontology for recommended plants suitable for individual farmers makes a contribution to the knowledge management field. Besides being useful in DSS by offering options with accuracy, it also reduces the complexity of the problem by reducing decision variables and condition variables in the multi-objective optimization model of DSS.