JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE THEORY AND PRACTICE
- P-ISSN2287-9099
- E-ISSN2287-4577
- SCOPUS, KCI
7권 3호
초록
Abstract
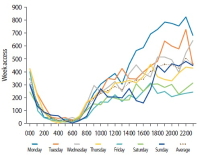
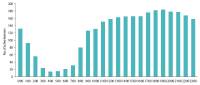
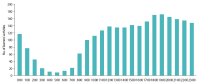
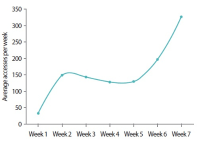
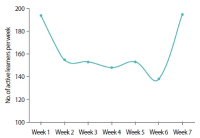
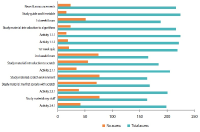
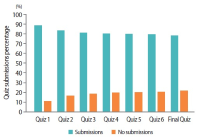
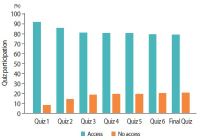
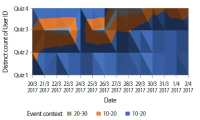
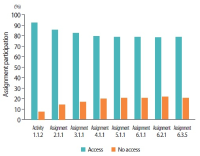
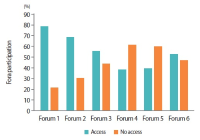
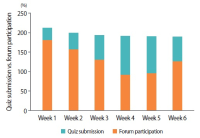
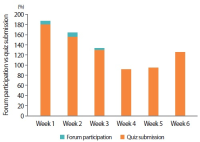
Learning analytics, or educational data mining, is an emerging field that applies data mining methods and tools for the exploitation of data coming from educational environments. Learning management systems, like Moodle, offer large amounts of data concerning students’ activity, performance, behavior, and interaction with their peers and their tutors. The analysis of these data can be elaborated to make decisions that will assist stakeholders (students, faculty, and administration) to elevate the learning process in higher education. In this work, the power of Excel is exploited to analyze data in Moodle, utilizing an e-learning course developed for enhancing the information computer technology skills of school teachers in primary and secondary education in Greece. Moodle log files are appropriately manipulated in order to trace daily and weekly activity of the learners concerning distribution of access to resources, forum participation, and quizzes and assignments submission. Learners’ activity was visualized for every hour of the day and for every day of the week. The visualization of access to every activity or resource during the course is also obtained. In this fashion teachers can schedule online synchronous lectures or discussions more effectively in order to maximize the learners’ participation. Results depict the interest of learners for each structural component, their dedication to the course, their participation in the fora, and how it affects the submission of quizzes and assignments. Instructional designers may take advice and redesign the course according to the popularity of the educational material and learners’ dedication. Moreover, the final grade of the learners is predicted according to their previous grades using multiple linear regression and sensitivity analysis. These outcomes can be suitably exploited in order for instructors to improve the design of their courses, faculty to alter their educational methodology, and administration to make decisions that will improve the educational services provided.






초록
Abstract
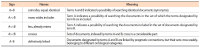
Information about the formation and filling (in 2014 to 2016) of a terminological dictionary on electronics and radioengineering and collective work (in 2017 to 2018) with a data bank “TERMIN” is presented in this article. In purpose of creating an instrument of navigating the modern scientific-technical space a net of terms with set semantic links is described. This set is based on the analysis of terms’ definitions (each term is checked for inclusion in the definitions of all other terms; the definitions were borrowed from reputable reference editions: encyclopedias, dictionaries, reference books). The created model of a system that consists of different information sources, in which it (information) is indexed by the terminology of Russian State Rubricator of Scientific and Technical Information rubrics and/or keywords, is described. There is an access for the search in all these sources in the system. Searching inquiries are referred to in the language of these rubrics or formulated by arbitrary terms. The system is to refer to information sources and give out relevant information. In accordance with this model, semantic links of various types, which allow expanding a search at different modalities of query, should be set among data bank terms. Obtained links will have to increase semantic matching, i.e., they can provide actual understanding of the meaning of the information that is being sought.

초록
Abstract
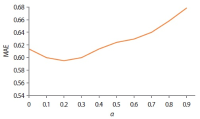
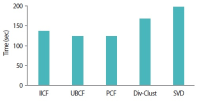
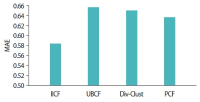
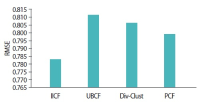
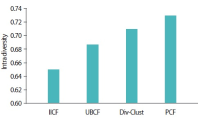
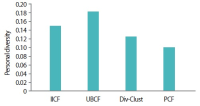
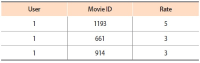
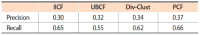
Nowadays, recommender systems suggest lists of items to users considering not only accuracy but also diversity and novelty. However, suggesting the most diverse list of items to all users is not always acceptable, since different users prefer and/or tolerate different degree of diversity. Hence suggesting a personalized list with a diversity degree considering each user preference would improve the efficiency of recommender systems. The main contribution and novelty of this study is to tune the diversity degree of the recommendation list based on the users’ variety-seeking feature, which ultimately leads to users’ satisfaction. The proposed approach considers the similarity of users’ desire diversity as a new parameter in addition to the usual similarity of users in the state-of-the-art collaborative filtering algorithm. Experimental results show that the proposed approach improves the personal diversity criterion comparing to the closest method in the literature, without decreasing accuracy.


초록
Abstract
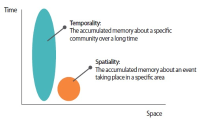
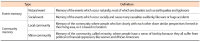
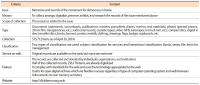
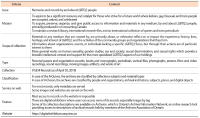
Until now, records re-enacting social memories have not been main targets for preservation and management in Korea. However, people have recently begun to focus on forming and maintaining their memories because these personalized records have started to be recognized as social and political issues. In this respect, this study aims to find out how to preserve social memories by comparing various global open archives. For achieving our research goal, we first established the definition of social memories and records and revealed their characteristics. After then, we selected representative open archives’ websites to examine their collection polices and compare them according to several criteria. As a result, we distilled insights based on similarities and differences of each archive and discussed considerations in preserving social memories consisting of three phases: analyzing target social memories, establishing collection policies, and collecting actual records. This study has significance in that it examines the characteristics of social memories and records and also suggests preliminary findings for advanced research to develop practical tools for social records management and archives.






초록
Abstract
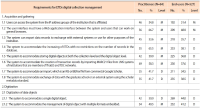
This research was aimed at studying the situation, problems, and requirements for digital collection lifecycle management of Thai theses and dissertations. The mixed research method used was composed of: (1) Study of the problem and situation in which the qualitative method was applied. The research site covered 10 higher education institutions where the Thailand Digital Collection (TDC) project is operated. The informants were key administrative officers of the TDC project of each institution. In-depth and structured interviews were conducted on an individual basis to obtain the most accurate answers. (2) Study of requirements based on the quantitative research method to survey the requirements for the digital collection management system for Thai theses and dissertations from 84 purposively-selected TDC project officers and 527 end users selected by accidental sampling, totaling 611 samples. Research findings are as follow: (1) The study of the situation and problems of digital collection lifecycle management shows that Thai higher institutions systematically manage their digital collection. The management lifecycle is consistent with the Guidance documents for lifecycle management of ETDs, which included seven steps: program planning, creation, submission, and ingestion, access and retrieval of digital objects, archiving and preservation, evaluation and assessment, inter-operation (creation of institutional collaboration), and development of link data. (2) The study of requirements for digital collection management of Thai theses and dissertations shows five system requirements: acquisition and gathering, digitization, metadata standards, management of rights, and storage and retrieval, all of which are at M (mandatory) and D (desirable) levels.