JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE THEORY AND PRACTICE
- P-ISSN2287-9099
- E-ISSN2287-4577
- SCOPUS, KCI
10권 2호
초록
Abstract
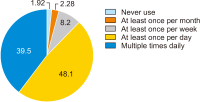
This study aimed to understand young adults’ attitudes concerning news and news resources they consumed, and how they encounter the fake news phenomenon. A qualitative approach was used with semi-structured interviews with 41 young adults (aged 20-30) in Tehran, Iran. Findings revealed that about half of the participants favored social media, and a smaller group used traditional media and only a few maintained that traditional and modern media should be used together. News quality was considered to be lower on social media than in traditional news sources. Furthermore, young adults usually followed the news related to the issues which had impact on their daily life, and they typically tended to share news. To detect fake news, they checked several media to compare the information; and profiteering and attracting audiences’ attention were the most important reasons for the existence of fake news. This is the first qualitative study for understanding news consumption behavior of young adults in a politicized society.
초록
Abstract
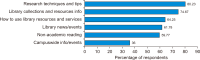
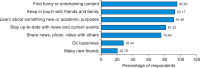
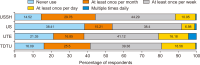
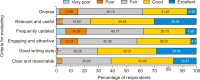
Facebook is very popular among young people and especially university students. Therefore, Facebook is the most logical platform to be used by academic libraries for promotional purposes and reaching out to user communities. This study aims to measure the effectiveness of using Facebook in connecting with students in academic libraries. A questionnaire survey was conducted to collect research data from students at four Vietnamese universities. A total of 1,670 valid questionnaires were returned, and more than half of the respondents were females between the ages of 18 and 22 years. The survey results found that libraries’ Facebook pages did not receive adequate attention and interaction from students. Besides that, the information needs of students and social media content in general affected student acceptance of libraries’ Facebook pages. These factors are demonstrated by the great majority of students who used Facebook often for various purposes, but fewer accessed library pages and they were not actively engaged in library posts. Students were interested in the information they already tended to get from libraries and were optimistic about the quality of library posts. However, they still expected more diverse and attractive content from the libraries. The findings of this study can help libraries create a close connection with students by satisfying their needs and expectations on Facebook.



초록
Abstract
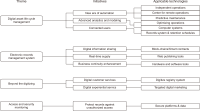
The primary function of an electronic records management system (ERMS) is to support organisations in providing effective records management services by enabling efficient remote access to the organisations’ records. This helps the organisation to continue running during emergency events, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. The need to study ERMS for accessing records remotely has increased dramatically, due to the increase in daily use. The situation arising from the COVID-19 pandemic has increased the need for implementing proper digital systems, such as ERMS, to enable efficient work processes and enhance business continuity. An ERMS has the potential to allow organisations to create records and workflows off-site. During a pandemic, the ability to structure processes digitally helps in maintaining operations remotely. This study aims to provide a narrative review of the ERMS literature with an emphasis on explaining the primary components of ERMS that act as enablers for the implementation of the system in the oil and gas sector of developing countries. The current study proposes ERMS roles and responsibilities that could enhance business continuity. The authors use a qualitative narrative review and analyse the literature related to this study and its findings. The results show that, in cases of risk or crises, staff members need to have easy access to their records and documents to remain productive. An ERMS allows professionals to remain active and work off-site. Thus, ERMS play a significant role in protecting an organisation’s content through the monitoring and control over who has authorisation to access its records.

초록
Abstract
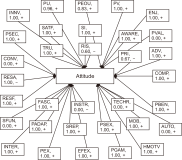
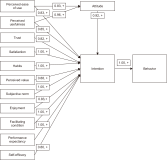
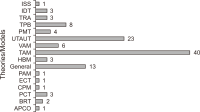
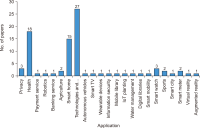
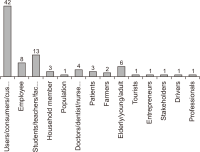
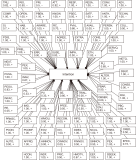
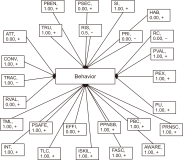
The research in the literature review on Internet of Things (IoT) adoption from an individual consumer viewpoint is minimal and has not yet been fully investigated. Therefore, the objectives of this study are to analyze the growth of IoT in recent years and to conduct a weight analysis of the factors that affect acceptance intentions and real usage of IoT-enabled services. For the review, we analyzed 87 publications from 13 conferences and 54 journals published during the period 2014-2020 about consumer adoption of IoT. Following the study, we discovered an unprecedented increase in the number of articles published in the last seven years, which points to an emerging area with an enormous prospect. Furthermore, the weight analysis outcome was associated with the diagrammatic representation in this study. After that, this research developed a generalized consumer IoT adoption model based on the 12 best predictors derived from frequency count and weight analysis, which had the highest predictive power for calculating IoT adoption. This paper further acknowledges the study’s theoretical and practical contributions, as well as its shortcomings, and proposes further research directions for future researchers.




초록
Abstract
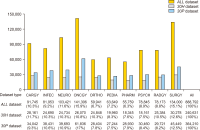
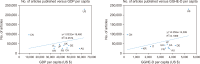
This study aimed to investigate publication productivity in various medical specialties in the top 10 countries with the highest number of published journal articles, considering the distinction between prolific and prestigious journals. For this study, we selected 10 specialties from the Scientific Journal Rankings (SJR) and used journals listed in both SJR and PubMed. Bibliographic details of these journals’ articles published from 2017 to 2019 were downloaded from PubMed. The results showed that various aspects of medical publication output were influenced by country characteristics such as specialty, journal type, population size, wealth, and healthcare expenditure. China showed the greatest variability in terms of specialty, as its publications in Oncology (ONCGY) were exceptionally high compared with the specialties of other countries. China’s publications in ONCGY exceeded even those of the United States in ONCGY. Furthermore, the western countries, the United Kingdom, Canada, and the United States in particular published more articles in prestigious journals than the other top 10 countries, where the East Asian countries published more articles in prolific journals than in prestigious journals.

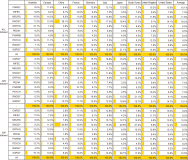

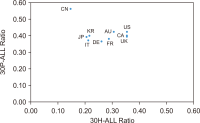
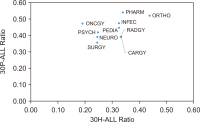
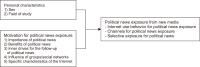
초록
Abstract
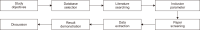
This research aimed at studying the factors that influence new media exposure of political news by youths in Isan society in Thailand. The target group comprised 1,200 individuals, obtained from multi-stage sampling from undergraduate students in Isan’s autonomous universities, governmental universities, and private institutions. The data collection tool was a questionnaire, the content of which was validated by experts. The reliability of the tool was tested by the formula for Cronbach’s alpha coefficient, which yielded a reliability of 0.83. Multiple regression analysis was applied to analyze the data. The results, regarding factors influencing the channels for political news exposure, showed that channels for political news exposure were mostly influenced by inner drives, followed by importance in political news exposure, influence from social networks, and specific characteristics of the Internet. This could explain the variation of channels for political news exposure at 46.5%. In terms of factors influencing political news selection, it was found that political news selection was influenced mostly from social networks, followed by inner drives, benefits from political news exposure, specific characteristics of the Internet, and the field of study. The variation of the political news selection could be explained at 44.6%. These results elaborate on the current situation in Thailand, especially in Isan region, where youths in higher education are playing an increasing role in demonstrating their political stance through various political activities.

